Brief study of the cell. History of the study of the cell
The vast majority of cells are microscopically small and cannot be seen with the naked eye. It was possible to see the cell and start studying it only when microscope invented. The first microscopes appeared at the beginning of the 17th century. For scientific research The microscope was first used by the English scientist Robert Hooke (1665). Examining thin sections of cork under a microscope, he saw numerous small cells on them. These cells, separated from each other by dense walls, Hooke called cells, using the term "cell" for the first time.
In the subsequent period, which covered the second half of the 17th century, the entire 18th century. and early XIX in. the microscope was improved and data were accumulated on animal and plant cells. towards the middle 19th century The microscope was greatly improved and much became known about the cellular structure of plants and animals. The main materials on the cellular structure of plants at that time were collected and summarized by the German botanist M. Schleiden.
All the data obtained about the cell served as the basis for the creation cell theory the structure of organisms, which was formulated in 1838 by the German zoologist T. Schwann. Studying the cells of animals and plants, Schwann found that they are similar in structure, and established that the cell is a common elementary unit of the structure of animal and plant organisms. Schwann outlined the theory of the cellular structure of organisms in the classic work "Microscopic studies on the correspondence in the structure and growth of animals and plants."
At the beginning of the last century, the famous scientist, academician Russian Academy Karl Baer discovered the egg cell of mammals and showed that all organisms begin their development from a single cell. This cell is a fertilized egg, which is crushed, forms new cells, and tissues and organs of the future organism are formed from them.
Baer's discovery complemented the cell theory and showed that the cell is not only a unit of structure, but also a unit of development of all living organisms.
An extremely significant addition to the cellular theory was the discovery of cell division. After the discovery of the process of cell division, it became quite obvious that new cells are formed by dividing existing ones, and do not arise anew from non-cellular matter.
The theory of the cellular structure of organisms also includes the most important materials for proving the unity of the origin, structure and development of everything organic world. F. Engels highly appreciated the creation of the cellular theory, putting it in value next to the law of conservation of energy and the theory natural selection Ch. Darwin.
To late XIX in. The microscope was improved so much that it became possible to study the details of the structure of the cell and its main structural components were discovered. At the same time, knowledge about their functions in the vital activity of the cell began to accumulate. By this time, the emergence of cytology, which is currently one of the most intensively developing biological disciplines, dates back.
Methods for studying cells. Modern cytology has numerous and often quite complex research methods that have made it possible to establish the fine details of the structure and reveal the functions of a wide variety of cells and their structural components. An exceptionally large role in cytological research continues to be played by the light microscope, which today is a complex, perfect instrument, giving an increase of up to 2500 times. But even such a large magnification is far from sufficient to see the fine details of the cell structure, even if we consider sections 5–10 cm thick. µm 1 dyed with special dyes.
Absolutely new era in the study of the structure of the cell began after the invention electron microscope, which gives an increase of tens and hundreds of thousands of times. Instead of light, the electron microscope uses a fast flow of electrons, and the glass lenses of the light-optical microscope are replaced in it. electromagnetic fields. Electrons flying at high speed are first concentrated on the object under study, and then they fall on a screen similar to a TV screen, and on it you can either observe an enlarged image of the object or photograph it. The electron microscope was designed in 1933, and has become especially widely used for the study of biological objects in the last 10–15 years.
For examination in an electron microscope, cells are subjected to very complex processing. The thinnest sections of cells are prepared, the thickness of which is 100–500 A. Only such thin sections are suitable for electron microscopic examination due to their low permeability to electrons.
AT recent times more and more chemical methods are being used to study the cell. A special branch of chemistry - biochemistry today has numerous subtle methods that allow you to accurately determine not only the presence, but also the role of chemicals in the life of the cell and the whole organism. Created complex devices called centrifuges, which develop a huge speed of rotation (several tens of thousands of revolutions per minute). With the help of such centrifuges, it is easy to separate the structural components of the cell from each other, since they have different specific gravity. This one is very important method makes it possible to study separately the properties of each part of the cell.
The study of the living cell the finest structures and functions is a very difficult task, and only a combination of efforts and colossal work of cytologists, biochemists, physiologists, geneticists and biophysicists made it possible to study in detail its structural elements and determine their role.
The basic structural and functional unit of any living organism is the cell. Only viruses, whose position in the living system is not entirely clear, lack a cellular structure. A cell can exist either as a separate (unicellular) organism (bacteria, protozoa, many algae and fungi), or as part of the body of multicellular animals, plants and fungi. But even in the largest organisms, each of its billions of cells is relatively independent and performs a specific function.
The history of the study of the cell is inextricably linked with the development of research methods, primarily with the development of microscopic techniques. The first simple microscope appeared at the end XVI century. It was built in Holland. About the device of this magnifying device it is known that it consisted of a pipe attached to a stand and having two magnifying glass. The first to understand and appreciate great value microscope, was the English physicist and botanist Robert Hooke. He was the first to use a microscope to study plant and animal tissues. In 1665, Robert Hooke first described the structure of some plant tissues, in particular cork, consisting of small cells bounded by partitions, in his essay "Micrography, or some physiological descriptions of the smallest bodies made by means of magnifying glasses." Thus the cage was opened. Studying a cut prepared from cork and elderberry core, R. Hooke noticed that they include many very small formations, similar in shape to honeycomb cells. He gave them the name of the cell or cell (Fig. 1). The term "cell" was established in biology, although R. Hooke did not see the cells themselves, but the shells of plant cells.
Through the efforts of many scientists, mainly XIX and the first half of the 20th century, developed special science about the cell, called cytology.
The optical instrument acquired the value of a valuable scientific instrument thanks to the improvements of the famous Dutch explorer Anthony van Leeuwenhoek. His microscope made it possible to see living cells at a magnification of 270 times.
"Biology. General biology. A basic level of. Grades 10-11 ". V.I. Sivoglazov (gdz)
History of the discovery and study of the cell. cell theory
Question 1. Tell us about the history of the discovery of the cell.
The discovery of the cellular structure of living organisms became possible thanks to the advent of the microscope. Its prototype was invented in 1590 by the Dutch glass grinder Zachary Jansen. The first microscope is known to have consisted of a tube attached to a stand and had two magnifying glasses.
The importance of the microscope for studying the structure of sections of plant and animal objects was first appreciated by the English physicist and botanist Robert Hooke. In 1665, on sections of cork, he discovered structures resembling honeycombs, and called them cells or cells. However, Hooke was wrong, believing that cells are empty, and living matter is cell walls.
Dutch naturalist Anthony van Leeuwenhoek in the second half of the 17th century. improved the microscope and was the first to see living cells. He observed and drew a number of protozoa, spermatozoa, bacteria, erythrocytes and even their movement in capillaries.
Question 2. By whom and when was the cell theory first formulated?
The study of plant and animal cells made it possible to generalize all the features of their structure. In 1838, M. Schleiden created the theory of cytogenesis (cell formation). His main merit is to raise the question of the origin of cells in the body. In 1839, T. Schwann, based on the work of M. Schleiden, created a cell theory. The main provisions of the cell theory (M. Schleiden and T Schwann):
1) all tissues are made up of cells;
2) plant and animal cells have common principles of structure, tk. arise in the same way;
3) each individual cell is independent, and the activity of the organism is the sum of the vital activity of individual cells.
In 1858, R. Virchow also paid great attention to the further development of the cellular theory. He not only brought together all the numerous disparate facts, but also convincingly showed that cells are a permanent structure and arise only through the reproduction of their own kind - “every cell comes from another cell as a result of division, just like a plant is formed from a plant, and from animals animals”, i.e. discovered cell division.
Question 3. List modern provisions cell theory.
In our time, cytology, using the achievements of genetics, molecular and physico-chemical biology, is developing very rapidly. And although the main provisions of the theory of T. Schwann and M. Schleiden remain relevant, the data obtained made it possible to form a deeper understanding of the structure and functions of the cell. Based on them, the modern cellular theory was formulated. We list its main provisions:
1) a cell is a unit of structure, functioning, reproduction and development of living organisms;
2) the cells of all organisms are similar in structure and chemical composition;
3) cell reproduction occurs by dividing the mother cell;
4) cells of multicellular organisms are specialized: they perform different functions and form tissues.
Question 4. Describe the importance of cell theory for the development of biology.
According to philosophers who have studied the history of science (for example, Friedrich Engels), cell theory is one of the greatest discoveries 19th century She played a huge role in the development of not only biology, but also natural science in general. Protozoa, bacteria, many fungi and algae are cells that exist separately from each other. The body of all multicellular organisms - plants, fungi and animals - is built from more or less cells, which are the elementary structures that make up a complex organism. Regardless of whether a cell is an integral living system or a part of it, it has a set of features and properties common to all cells.
The cell theory for the first time unequivocally pointed to the unity of the living world. With its appearance, the gap between the animal kingdom and the plant kingdom disappeared. Based on cell theory in mid-nineteenth in. Cytology arose - a science that studies the structure and functions of the cell.
Think for which representatives of the organic world the concepts of "cell" and "organism" coincide.
A cell is the basic structural, functional and genetic unit of the organization of living things, an elementary living system. A cell can exist as a separate organism.
The concepts of "cell" and "organism" coincide in the case when we are talking about unicellular organisms. These include prokaryotes, or non-nuclear ones (in particular, bacteria), and from eukaryotes, or nuclear ones, the simplest ones (such as ciliates shoe, chlamydomonas, green euglena). Their body consists of one cell, which implements all the functions of the body - metabolism, irritability, reproduction, movement. Various organelles contribute to these functions, including special purpose(for example, flagella and cilia provide movement). unicellular organisms often able to form clusters - colonies. However, the concept of a “multicellular organism” is still inapplicable to a colony, since its constituent cells have the same type of structure (they are not subdivided into tissues), weakly interact with each other and, being isolated from the colony, continue to exist and multiply independently without any problems.
Recall from sections 6 and 7 of the grades when the first studies of plant and animal cells began. What instruments are used to study the cellular structure of organisms?
Rice. 36. Robert Hooke's microscope and the section of cork he saw
Most organisms on Earth have a cellular structure. A cell is a structural and functional unit of the living, capable of self-reproduction, which is characterized by all the signs of the living.
The history of the discovery of the cellular structure of organisms. The cell was discovered in the middle of the 17th century. Then the English naturalist Robert Hooke (1635-1703) for the first time saw and described the cellular structure of plants using a microscope.
Examining a thin section of cork at high magnification of the microscope, Hooke was struck by its complex structure. He wrote: “Taking a piece of clean light cork, I cut off a very thin plate from it with a razor-sharp penknife. When I then began to examine it under a microscope, ... I clearly saw that it was all riddled with holes and pores ... These pores were not deep, but consisted of very many small cells, isolated from a continuous pore by special partitions. Such a structure is not characteristic of cork alone” (Fig. 36).
With these words, in 1665, Robert Hooke first reported the existence of the cell. He was also the first to use the term "cell" (cellula) to refer to the cell wall he saw. This term has firmly entered biology, and its discovery marked the beginning of the study of the cellular structure of organisms.
Further study of the cellular structure of organisms is associated with the name of the Dutch researcher A. Leeuwenhoek. The lenses made by the scientist gave a magnification of 300 times, which made it possible to make a number of great discoveries: to describe bacteria, protozoa (ciliates), erythrocytes, spermatozoa. After the publication of his research, Leeuwenhoek became widely known as the greatest scientist of his time (Fig. 37).
![]()
Rice. 37. Anton van Leeuwenhoek (1632-1723)
Creation of the first cell theory. Cells began to be studied especially intensively in the 19th century, which was associated with the improvement of microscopes. In 1939, summarizing numerous microscopic studies cells, German scientists zoologist Theodor Schwann and botanist Matthias Schleiden (Fig. 38) formulated the main provisions of the cell theory: 1) all organisms are made up of cells; 2) cells are the smallest structural units of life; 3) cells in the body arise by neoplasms from non-cellular substances.
In some conclusions, scientists were wrong. In particular, the position on the emergence of new cells turned out to be incorrect. But the basic idea of the cellular structure of organisms was correct.
After the creation of the cell theory, cell research became leading in biology. Thanks to the work of many scientists, the structure of the cell nucleus was studied in detail, and the most important biological processes that occur with cells were analyzed. Particularly significant were the studies of the German physician and scientist Rudolf Virchow (Fig. 38), who corrected and supplemented the cellular theory. In 1858, he substantiated the principle of cell succession: "each cell comes from a cell by dividing the original cell."

Rice. 38. The founders of the cell theory (from left to right): Matthias Schleiden (1804-1881), Theodor Schwann (1810-1882) and Rudolf Virchow (1821 - 1902)
The cell theory has basically been formulated. However, the methods of studying the cell were imperfect, and the science of the cell had not yet taken shape as an independent scientific discipline.
Cytology is the science of the cell. On the turn of XIX-XX centuries a new section of biology arose and formed - cytology (from the Greek kitos - vessel, here - cell and logos - doctrine) - a science that studies the structure and functions of cells. Further development this science was directly related to discoveries in physics, chemistry and the improvement of microscopic technology.

Rice. 39. Microscopes: 1 - light; 2 - electronic. Images of cells obtained from different microscopes: 3 - light; 4 - electronic
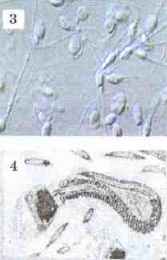
Currently, to study cells, scientists use various methods. The microscopy method makes it possible to study in detail the appearance of cells, their microstructure (Fig. 39). In a light microscope, you can see fairly large organelles, such as the nucleus, mitochondria, chloroplasts, the Golgi apparatus. An electron microscope gives a magnification 1000 times greater than a light microscope, which allows you to examine in detail the structure of individual organelles.
With the help of physicochemical and biochemical methods, organic and inorganic substances of the living, their functions and pathways of transformations in the cell have been studied. The use of cell and tissue culture methods made it possible to observe the growth and reproduction of cells outside the body, to isolate growth factors, to determine the effect of various substances on cells, and to obtain cell hybrids by cell fusion.
The main provisions of modern cell theory:
- a cell is a structural and functional unit of the living, which is an elementary living system, which is characterized by all the main features of the living;
- cells of all organisms have a similar chemical composition and general structural plan;
- a new cell arises as a result of the division of the original cell;
- multicellular organisms develop from a single source cell;
- the similarity of the cellular structure of organisms indicates the unity of their origin.
The light microscope was significantly improved in the period from 1887-1900. The development of chemistry and biochemistry has led to the development of new methods for fixing and staining micropreparations. From that moment on, cytology as a science acquired an experimental character. In 1930, an electron microscope was constructed, which made it possible to study the ultrastructure of the cell.
Lesson learned exercises
- By whom and when was the cellular structure of organisms first discovered?
- Name the authors of the first cell theory and formulate its main provisions.
- Why did it take about 200 years from the discovery of cells to the formation of cell theory?
- What does cytology study?
- What methods are used by modern cytologists?
- What are the advantages of an electron microscope over a light microscope?
- Burns, Robert - short biography
- The concept of common vocabulary and vocabulary of limited use
- Nancy Drew: The Captive Curse Walkthrough Nancy Drew Curse of Blackmoore Manor Walkthrough
- Deadpool - Troubleshooting
- Won't start How to Survive?
- What to do if bioshock infinite won't start
- Walkthrough Nancy Drew: Alibi in Ashes
- Spec Ops: The Line - game review, review Spec ops the line crashes on missions
- Room escape level 1 walkthrough
- Processing tomatoes with boric acid How much will 2 grams of boric acid
- Cucumber Grass (Borago)
- Bioinsecticide Lepidocid: purpose, properties and application procedure Lepidocide waiting period
- How to change the language to Russian in steam
- Dendrobium noble: room care
- Morphology of plants general concepts - document
- Planting, propagation and care of bamboo at home, photo Growing bamboo from seeds
- How to strengthen the cellular signal for the Internet in the country
- Sanskrit reveals the forgotten meaning of Russian words (2 photos)
- The oldest language Sanskrit programming language of the future Dead language Sanskrit
- Who has dominion over all the earth?









