What are all living organisms made of? cell theory
Living beings differ from inanimate nature not only in their metabolism (although this is their most significant, most important difference), but also in their structure.
All living organisms are made up of cells. Only viruses that cause some infectious diseases (for example, influenza, measles, smallpox) are not themselves cells and do not consist of cells. But they can reproduce only in a living cell.
First look at cells
The cell was first discovered by the English physicist Robert Hooke in 1665.
Hooke designed microscopes that gave a magnification of 140 times. Once, when examining thin sections of cork, he saw that the entire cork consists of cells, or pores. These were the cells. By publishing his observation, Hooke initiated study of the cellular structure of the living world. But in his descriptions there was not even a hint of the idea of a cell as the basic structural unit of any living organism. It was just a story about the cellular structure of cork.
The idea of \u200b\u200bthe patterns of structure and development of plants and animals
Only almost 200 years later, in 1834, the Russian scientist P.F. Goryaninov put forward the idea of a general regularity in the structure and development of plants and animals. He believed that all living organisms are composed of interconnected cells. Accumulations of cells make up tissues that can change during growth and development. This idea was confirmed in the works of German scientists - the botanist Matthias Schleiden and the zoologist Theodor Schwann, who, having collected a large factual material, formulated the cellular theory of the structure of plants and animals. cell theory- one of the most important discoveries of mankind. Engels believed that the law of conservation of energy, the cellular theory and Darwin's theory of evolution are three greatest discoveries 19th century
cell theory
The cell theory proved the general structure of plants and animals. By studying various living tissues, scientists were convinced that all living things are made up of cells. As the microscope improved, the cell was subjected to more and more in-depth study. AT last years With the help of electron microscopes, giving a magnification of hundreds of thousands of times, it became possible to study internal structure cells. Although the cell is considered the simplest structural unit of a living being, in itself it is a very complex system. Metabolism, energy conversion, biosynthesis take place in the cell, it has the ability to reproduce, irritability, that is, it can respond to changes in environmental conditions. To better visualize the cell, look at the diagram of its structure, observed in electron microscope
In the human body there are a variety of cells that differ from each other in structure and function. For example, the cells that make up the muscles are elongated, they have special threads (fibrils) that can contract. And skin cells (epithelial tissue) resemble elongated cubes and stand in dense rows. Fat cells are round and filled with droplets of fat.
We will not list the entire variety of cells, we will only say that all cells of both the plant and animal world, despite their differences, have a similar structure. They always have a denser outer layer - a shell, cytoplasm and nucleus.
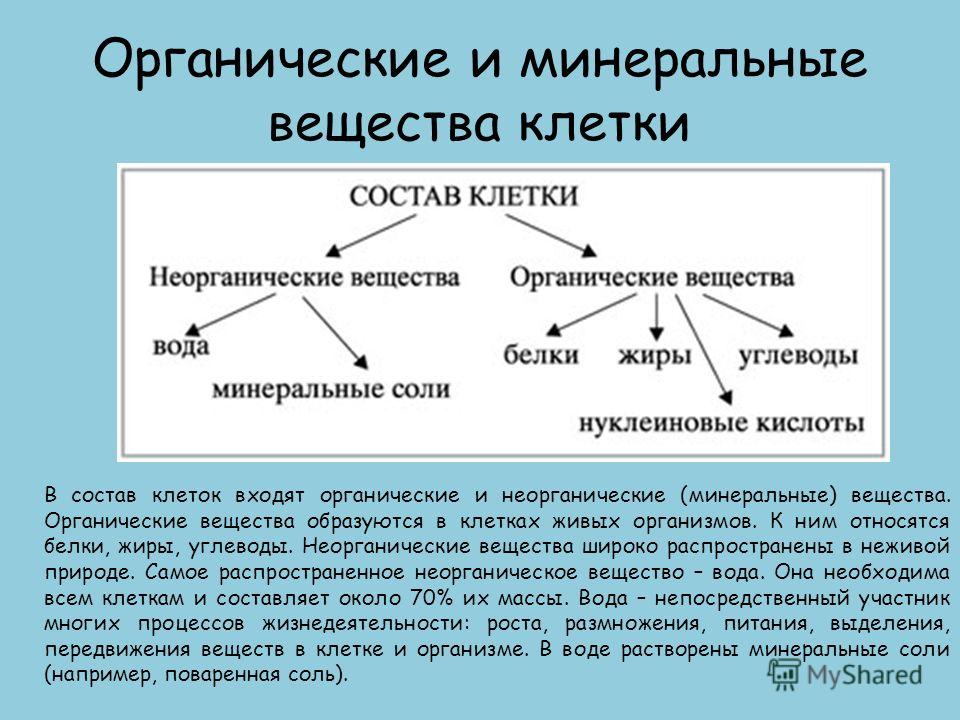
Organic and mineral substances of the cell Cells include organic and inorganic (mineral) substances. Organic substances are formed in the cells of living organisms. These include proteins, fats, carbohydrates. Inorganic substances are widely distributed in inanimate nature. The most common inorganic substance is water. It is necessary for all cells and makes up about 70% of their mass. Water is a direct participant in many life processes: growth, reproduction, nutrition, excretion, movement of substances in the cell and body. Mineral salts (for example, table salt) are dissolved in water.
Proteins Proteins are complex organic compounds. The bodies of living organisms are built from proteins. They are involved in all life processes. Vegetable proteins play an important role in the nutrition of animals and humans. Most proteins are found in plant seeds. Among animal proteins, everyone is familiar with the protein contained in chicken egg. Proteins of different structure in the cells of one organism can be several thousand species. animal protein vegetable protein (beans, peas, beans, soy and lentils)

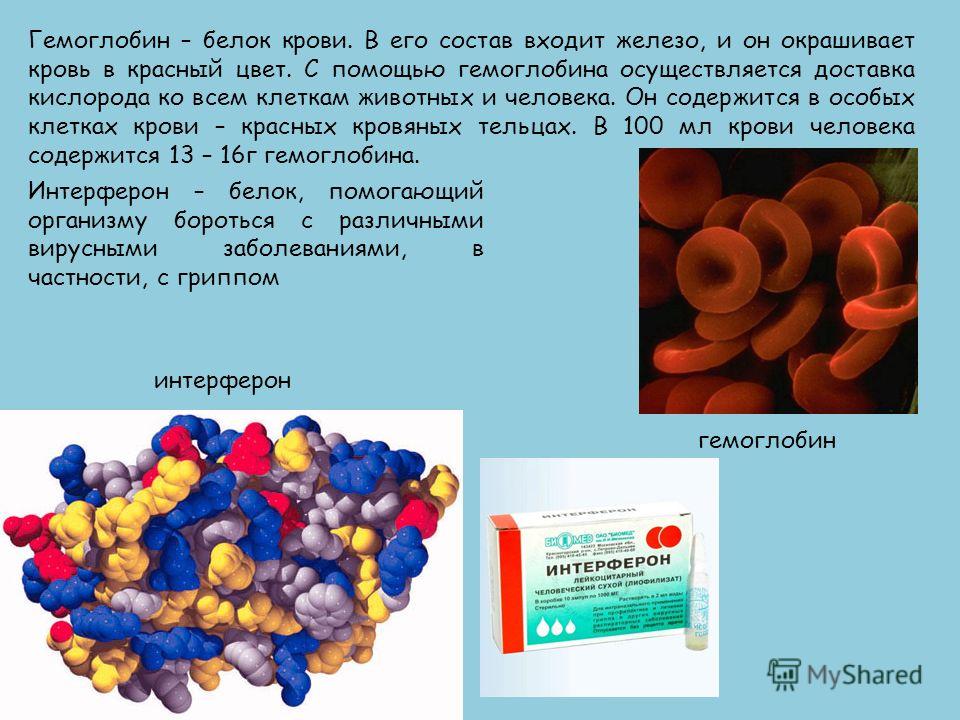
Hemoglobin is a blood protein. It contains iron, and it colors the blood red. With the help of hemoglobin, oxygen is delivered to all cells of animals and humans. It is found in special blood cells - red blood cells. 100 ml of human blood contains 13-16 g of hemoglobin. hemoglobin Interferon - a protein that helps the body fight various viral diseases, in particular, influenza interferon
Carbohydrates Carbohydrates are essential for all living organisms as a source of energy. These include glucose, sucrose, starch and other substances. Starch accumulates in potato tubers, banana fruits, wheat seeds. In many animals, carbohydrate glycogen is stored in the liver and muscles. Carbohydrates give strength to some parts of organisms: for example, they are part of the wood of plants. The carbohydrate chitin forms the outer covering of insects and crustaceans. chitin


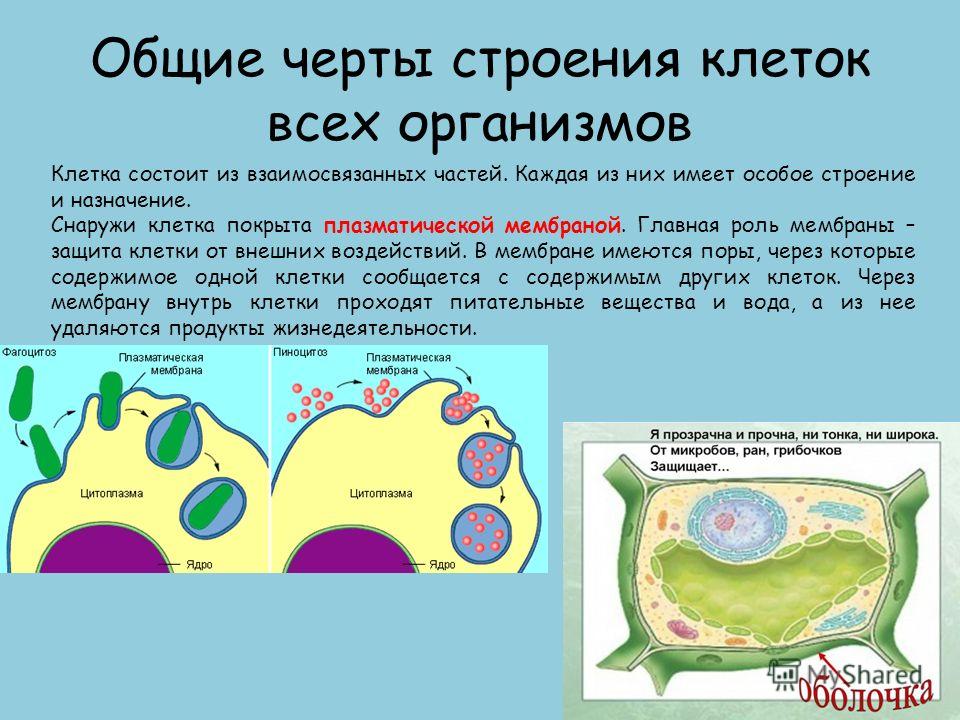
Common features structure of the cells of all organisms The cell consists of interconnected parts. Each of them has a special structure and purpose. Outside, the cell is covered with a plasma membrane. the main role membranes protect cells from external influences. The membrane has pores through which the contents of one cell communicate with the contents of other cells. Nutrients and water pass through the membrane into the cell, and waste products are removed from it.
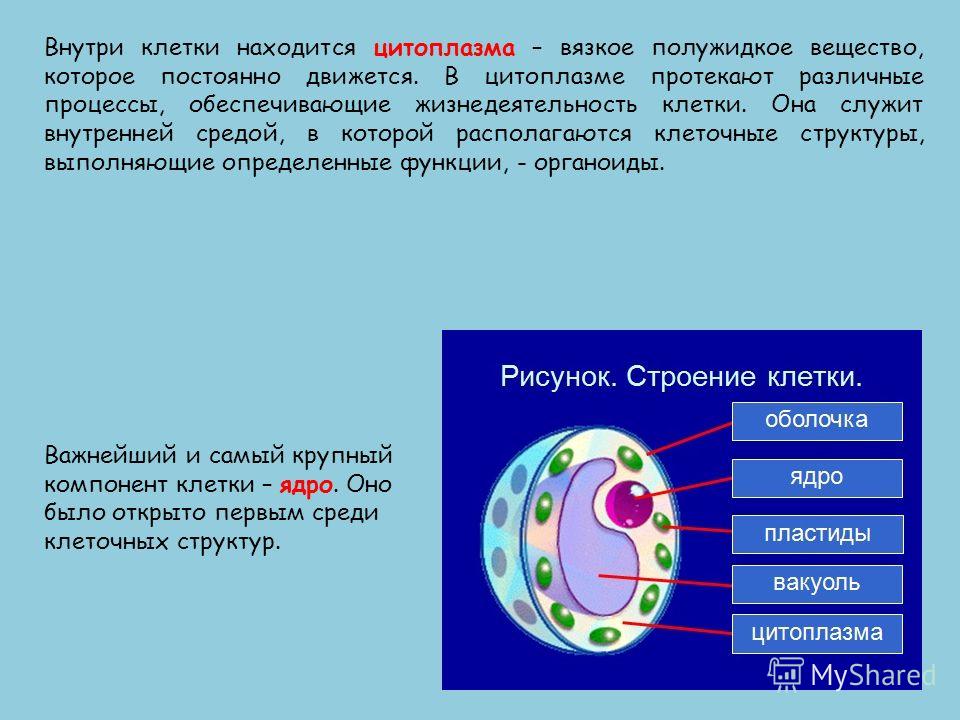
Inside the cell is the cytoplasm - a viscous semi-liquid substance that is constantly moving. Various processes take place in the cytoplasm that ensure the vital activity of the cell. She serves internal environment, in which cellular structures are located that perform certain functions - organelles. The most important and largest component of the cell is the nucleus. It was the first among cellular structures to be discovered.
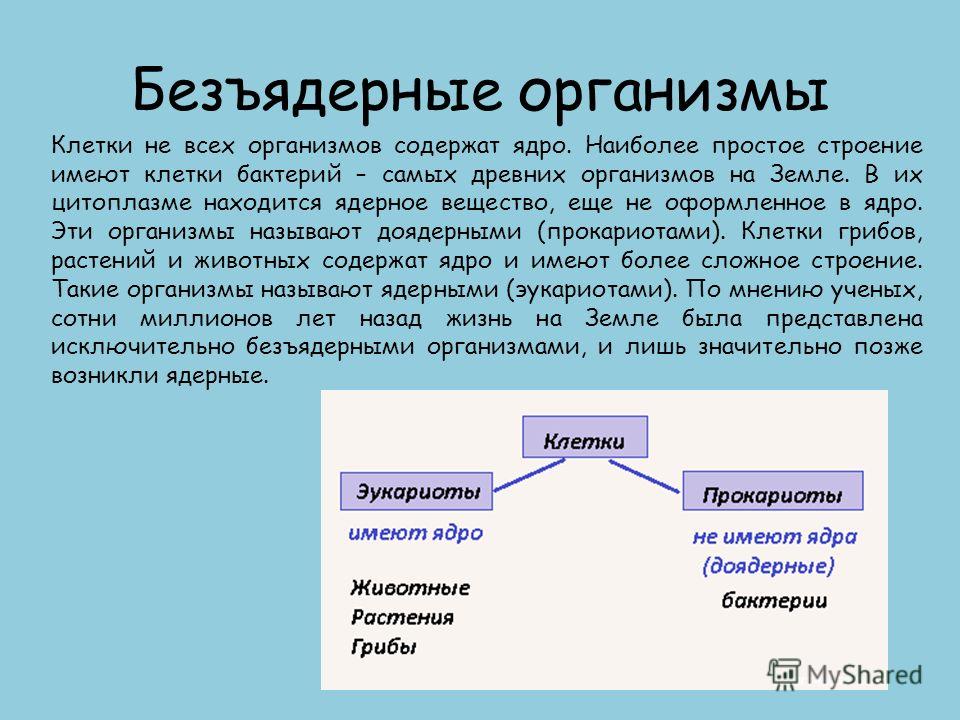
Non-nuclear organisms The cells of not all organisms contain a nucleus. Cells of bacteria, the most ancient organisms on Earth, have the simplest structure. In their cytoplasm there is a nuclear substance that has not yet been formed into a nucleus. These organisms are called pre-nuclear (prokaryotes). The cells of fungi, plants and animals contain a nucleus and have a more complex structure. Such organisms are called nuclear (eukaryotes). According to scientists, hundreds of millions of years ago, life on Earth was represented exclusively by non-nuclear organisms, and only much later did nuclear organisms arise.
Questions to e.g. 1. What substances are classified as organic, and which are inorganic? 2. What is the role of water in the cell? 3. What is the role of proteins, carbohydrates and fats in a cell? 4. What cell organelles do you know? 5. How are bacterial cells different from plant and animal cells?

All living organisms, with the exception of viruses, are made up of cells. Cells, most often represented by microscopic formations, have all the most important vital properties: self-regulation, self-reproduction, unity of structure and function, historical development etc. The processes of metabolism and energy conversion are constantly taking place in cells.
The science that studies the structure and functioning of cells is called cytology (from the Greek kytos - cell + logos - science). The development and formation of cytology was largely determined by the improvement of microscopic technology, since cells are difficult to study with the naked eye.
In 1665, the English naturalist R. Hooke first reported the existence of cells. He examined thin sections of cork under a microscope he had improved and found small empty pores and cells, which he called cells. Strictly speaking, in a cork section, R. Hooke observed dead cell walls, devoid of the living content that filled them. Examining various parts of other plants under a microscope, in particular carrots, burdock, ferns, he found the same structural plan as that of cork.
In 1677, M. Malpighi reported on the cellular structure of all the plants he studied. Prominent scientist of the 17th century. A. van Leeuwenhoek, examining a drop of water under a microscope, discovered protozoa unicellular organisms. For a long time, the shell was recognized as the main structural component of the cell.
After in early XIX in. there was a technical improvement in the quality of lenses, and attention to research using a microscope quickly increased. In 1825, the Czech scientist J. Purkinje showed that there is a gelatinous substance inside the cell, later called the cytoplasm. The English botanist R. Brown described the cell nucleus. The German botanist M. Schleiden in 1837 came to the conclusion that all plant cells contain nuclei.
In 1839, the German zoologist T. Schwann, summarizing his own experimental data and the results of other scientists, formulated the concept that is currently known as the cell theory. According to the cell theory: 1) the cell is the basic element of life; 2) any organisms consist of one or many cells. Indeed, despite the enormous diversity of living beings, differing in size (see table), shape, habitat, mode of movement, energy supply, etc., cells form the basis of their morphofunctional organization. R. Virchow in 1855 added a fundamental position to these two postulates: "Omnis cellula e cellulae" - "Every cell is from a cell." In other words, the third position of the cell theory states that all cells are formed only as a result of the division of other cells. The current content of cell theory can be briefly formulated as follows: the basic structural and functional unit of living organisms is the cell.
Note: 1 meter = 100 centimeters (cm); 1 cm = 10-2 m = 10 millimeters (mm); I mm = 10-3 m = 103 micrometers (µm); 1 µm = 10-6 m - 103 nanometers (nm); 1 nm = 10-9 m = 10-6 mm.
The cell theory is major achievement natural sciences. She played an outstanding role in the development not only of biology and medicine, but also of many other branches of human science.
Subsequent successes in cytology and cytogenetics were associated with the development and improvement of research methods. The central role of the nucleus in cell division was proved after the invention of the method of staining cytological preparations by W. Fleming in 1879. The improvement of light microscopes made it possible to obtain new information about the structure of the cell and some of its structures. However, the resolution of a light microscope is limited by the ability of the human eye, which can perceive separately two points at a distance of at least 0.1 mm. With this resolution, some cellular structures are not visible, and the study of others is significantly difficult.
A major step forward was the invention in the 30s. electron microscope by V. Zworykin and phase-contrast microscope by F. Zernike. The magnification of 100 thousand times, which is provided by the electron microscope, allows you to study the most small parts cell organelles. Modern achievements cytology and cytogenetics are associated with the development of chemical, physical methods and technologies (from X-ray diffraction analysis to computer databases).
In multicellular organisms, each cell is specialized to perform, as a rule, one of the functions necessary to ensure the vital activity of the organism as a whole.
Depending on the function performed, cells can vary significantly both in size, shape, location in various tissues and organs of the body, and in other external and internal characteristics.
Let us indicate the main types of specialization of cells of a multicellular organism. It:
Perception of external and internal stimuli;
Coordination of all functions (cells of the nervous and endocrine systems);
movement and support;
Protection of the body (cells of integumentary tissues and the immune system);
Obtaining nutrients or their synthesis;
Transfer of nutrients, biologically active substances, gases, etc.;
Removal of decay products; reproduction.
More on CELL THEORY:
- Cell cycle. Cell cycle regulator molecules open pathways for diagnosing and destroying cancer cells
At one time, having learned from one famous song that girls are made of "flowers, bells, notebooks and glances", I realized that I was doomed either to a crisis of gender identity, or to the suspicion that in reality everything was arranged somehow differently.
Yes, otherwise. Now I will try to explain.
"Composition" of life
I'll start from afar. Imagine that a person is such an anatomical nesting doll. From complex to simple: let's figuratively divide it into organs (literally, it is also possible, but this is usually a criminal offense). Bodies made up of tissue. And fabrics are made up of "details" - cells. Less cells molecules and atoms, but, being outside the cellular system, they do not form anything alive.
Cells- these are the "bricks" from which it is built any organism(even a girl, even a centipede).
Cells are similar, but they are not exactly the same. In one "set" (organism) there are many different parts, and every "detail" has its own role and its "content".
Standard cell device:
- cellular (plasma) membrane;
- cytoplasm;
- organelles;
- nucleus.
At membranes multiple functions. It insulates the contents of the cell from environment, but at the same time serves as a "door" for the passage of nutrients.
Cytoplasm- the liquid interior of the cell, where organelles and the nucleus float thoughtfully.
Nucleus- this is the "heart" in which the genetic material is stored. Always in cages eukaryote, but almost not formalized in prokaryotes. But DNA both have them and others. It's just that its "storage" in non-nuclear conditions is organized differently.
Varieties organelle a lot (vacuoles, plastids, Golgi complex, etc.), each has its own role.
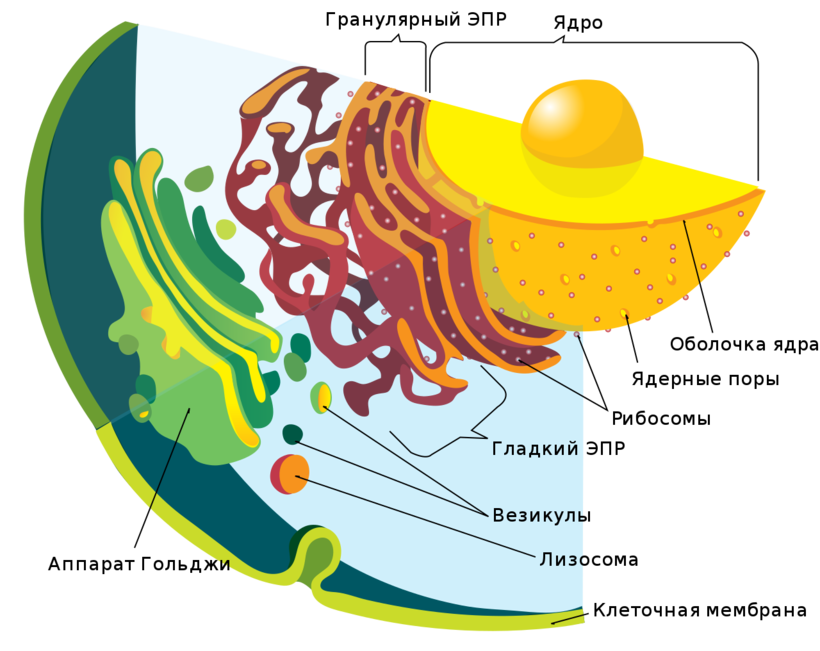
Inclusions- this is what "comes and goes" in the process of metabolism.
Cells are not just material. They feed, reproduce, die - they themselves alive!
Can you see them? Yes! Even a very simple microscope will help with this.
Cellular diversity of living organisms
In addition to complex multicellular creatures (like you and me), there are also very simple, unicellular. Like amoeba and ciliates. They are usually invisible due to their tiny size, but a microscope can help with that too. By the way, about microscopic. Even exceptionally small creatures (like tardigrade) are often quite themselves multicellular.
And the cells themselves are sometimes striking in size. Egg(this is the scale) - this is a huge fertilized egg

It's interesting that viruses who got a very unusual position between the living and the inanimate, acellular.
It remains unexplained until now. Although living beings contain the same chemical elements as inanimate bodies (carbon, nitrogen, hydrogen, oxygen, phosphorus, potassium, etc.), the development of living matter from inorganic matter requires the emergence of complex organic substances: carbohydrates, fats, proteins , nucleic acids.
Live nature organized very complex: organisms are part of populations - a complex of organisms inhabiting a homogeneous territory and interacting with each other. Populations of different species form communities (biocenosis). A community is a living component of an ecosystem - a single system in which living organisms and organic elements are connected, and in which the process of energy transfer from one stage to another and the circulation of substances take place. Ecosystem - part of the biosphere - a global ecosystem formed by the totality of all ecosystems of our planet.
Thus, living nature on our planet is a single whole, consisting of interconnected parts -cells, organisms, species, natural communities and ecosystems.
- The cell is the smallest unit of life. Below the level of the cell (at the level of individual organelles, molecules, atoms), the properties inherent in the living do not appear. In multicellular organisms, cells perform different functions and combine to form tissues and organs, which, in turn, form organ systems.
- Each organism belongs to its own species.
- Individuals of one species live in groups - populations.
- Living organisms different types exist on the same territory or water area, forming diverse communities - natural or man-made. Populations of different species living in a common area constitute a natural community.
- A natural community is a living part of an ecosystem. In ecosystems, there is a circulation of substances between living and non-living nature.
- Ecosystems together form the global ecosystem of the Earth - the biosphere. The biosphere is the geological shell of the Earth inhabited by livingorganisms, covering the surface layers of the earth's crust, the hydrosphere and the lower layers of the atmosphere.
Living organisms have a metabolism, heredity, irritability, the ability to reproduce and self-regulate, that is, they retain the main features of their structure. They are able to adapt to environmental conditions.
Metabolism and energy conversion
Necessary conditions for the existence of an organism - metabolism and energy conversion. In the process of nutrition, the body receives substances from external environment. They disintegrate, transform and deliver to every cell. They create organic substances rich in energy. For the breakdown of organic substances, oxygen is needed, which is supplied in the process of respiration. The energy released during decay is spent on the synthesis of new essential substances, on the processes of movement, growth, and development.
reproduction
Influence of abiotic factors
Any organism is affected by a complex of abiotic environmental factors: Material from the site
All these factors periodically change during various periods of time (hour, day, month, year, etc.) directly affecting the vital activity of organisms. In this regard, all organisms have certain mechanisms of adaptation to environmental conditions.
- Burns, Robert - short biography
- The concept of common vocabulary and vocabulary of limited use
- Nancy Drew: The Captive Curse Walkthrough Nancy Drew Curse of Blackmoore Manor Walkthrough
- Deadpool - Troubleshooting
- Won't start How to Survive?
- What to do if bioshock infinite won't start
- Walkthrough Nancy Drew: Alibi in Ashes
- Spec Ops: The Line - game review, review Spec ops the line crashes on missions
- Room escape level 1 walkthrough
- Processing tomatoes with boric acid How much will 2 grams of boric acid
- Cucumber Grass (Borago)
- Bioinsecticide Lepidocid: purpose, properties and application procedure Lepidocide waiting period
- How to change the language to Russian in steam
- Dendrobium noble: room care
- Morphology of plants general concepts - document
- Planting, propagation and care of bamboo at home, photo Growing bamboo from seeds
- How to strengthen the cellular signal for the Internet in the country
- Sanskrit reveals the forgotten meaning of Russian words (2 photos)
- The oldest language Sanskrit programming language of the future Dead language Sanskrit
- Who has dominion over all the earth?









