How does avs work. ABS (ABS) - anti-lock braking system
Before giving advice on how to properly brake with ABS, let's figure out what it actually is and what its purpose is. And here it is necessary to turn to the course of physics for the 9th grade.
ABS and classical mechanics?
When driving, the wheels of the car are constantly in contact with the road surface with a part of their area, which is called the contact patch. Thus, the wheels (and, consequently, the entire car) during its movement are constantly affected by the static friction force. Since it is greater than the sliding friction force, it prevents the wheel from slipping. Therefore, it is logical to use the static friction force, and not the sliding friction force, to stop the car.
What happens when we press the brake pedal? The driving wheels of the car are blocked and stop rotating, a sliding friction force begins to act on them, which, although less than the above-mentioned static friction force, is quite enough on roads with a good, dry surface. Well, what if it rained, or there were frosts at night, or under the wheels of your car is not asphalt, but a muddy primer? Then with a sharp press on the pedal, you can easily send your car into a skid. It is to prevent this situation that it exists.

How does ABS work?
The modern ABS system is complex, consisting of three main elements:
- speed sensors installed on the hub of each wheel of the car;
- pressure valves that distribute it along the brake line individually to each wheel;
- a control unit that receives signals from speed sensors and, having processed the information, distributes pressure (braking force) to each wheel.
Required trip condition ABS systems– a depressed pedal and at least one locked wheel. As soon as the speed sensor (one or more) signals that the wheel has stopped rotating and the sliding friction force has begun to act on it, it eliminates the braking force, allowing the wheel to rotate, but at a lower speed, since the first brake impulse has time to extinguish a little speed.

As soon as the braking force ceases to act on the wheel, it begins to rotate at a certain speed, which is again read by the sensor on the wheel hub, transmitting data to the control unit. That, in turn, having analyzed it according to a complex algorithm and finding it not low enough, transmits another braking impulse to the wheel, but at the same time chooses a force in such a way that braking is carried out on the verge of blocking - that is, the wheel does not completely stop.
On auto courses, you must have been warned against pressing the brake pedal to the floor, since this is what leads to a skid. On cars with ABS, it is better to forget about this rule. As soon as you feel the need for sudden braking, immediately squeeze out the brake and clutch pedals to the stop. Yes, yes, do not forget about the clutch, because it is necessary to completely exclude the engine from the braking process.
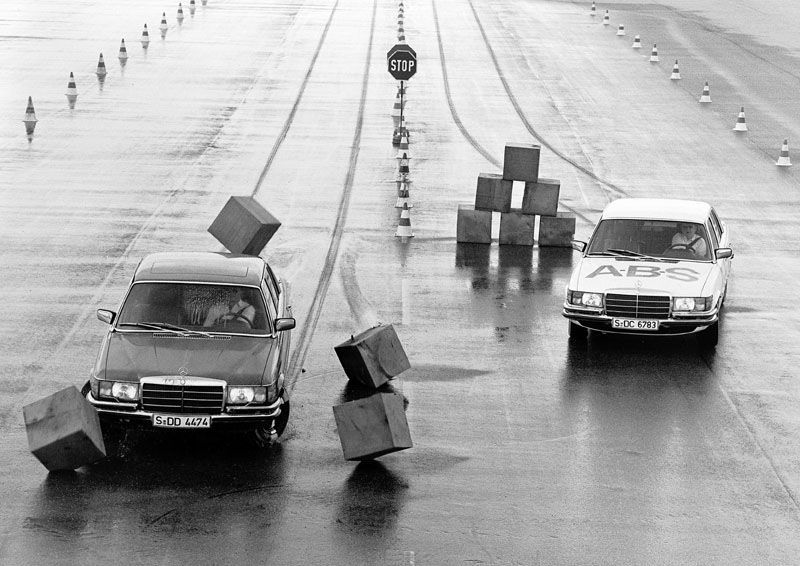

Do not try to use brake pulsations - ABS will do it for you and better than you. Your task is to press two pedals into the floor as sharply as possible and not release them until they come to a complete stop. At the same time, all the time you brake, you will hear a terrible rattle - the result of the ABS system - take it for granted.
If you need to stop abruptly, even on difficult icy conditions, then you need to do this as sharply as possible in order to anti-lock system worked instantly and you did not lose control of the car. During braking, try to steer yourself, keeping the car on a slippery track and avoiding collisions. After all, this is the main plus of the ABS system - it leaves you the ability to drive a car.
When is ABS useless?
It is important not only to know how to properly brake with ABS, but also to be able to identify situations where you cannot rely on the system, and therefore you can only rely on your own strengths and skills.
Video of testing a car with and without ABS:
On ABS, it will most likely become a hindrance, since it starts to work with some delay. The release of the brake pads occurs at the moment when the wheel is on the “approach”, respectively, when it lands, it moves for some time before the next ABS brake impulse begins to act on it again.
Approximately the same thing happens on roads with a mixed surface, for example, on partially icy or, where sections of dry and wet asphalt, snow and ice alternate. The ABS system simply does not have time to respond to changing conditions in a timely manner, so it is better to keep your distance and speed limit.
On loose surfaces (sand, gravel), a car with an anti-lock braking system slows down worse than without it. The point here is that the shaft in front of it, heated by the blocked wheel, plays the main role in braking. In the case of ABS, this does not happen and the braking distance is noticeably lengthened.
Also, anti-lock does not work at low speeds, usually below 7-10 km, so you should be more careful on slippery slopes. In general, as experienced car owners say, it is best to avoid the operation of the ABS - this is the most reliable way!
If you have your own ideas on this topic, we invite you to share your thoughts and experiences in the comments!
- News
- Workshop
In Canada, they created the perfect transport for the metropolis
Despite the frivolous appearance, the Solo electric car may well claim to be the ideal vehicle for the metropolis. As statistics show, the vast majority of motorists most often drive alone, therefore, the Solo single-seat layout is fully justified. The rejection of second place made it possible not only to make the electric car compact, but also to equip it with...
Russian car market: minus againMoreover, the fall is sometimes measured in double digits. For example, in August it was minus 18%, and in July - minus 16%. Against this background, September figures are perceived almost as a success - "only" minus 10.9%. However, we recall that this is minus eight compared to September 2015, which amazed everyone...
May is coming: cars began to rise in price
Thus, in the period from March 15 to April 15, the price tag for their products was rewritten by the majority of companies represented on the Russian market. Such data are provided in the study of the analytical agency "Avtostat", covering 47 automakers. Most of all, the price increase affected the Ford brand - the company increased prices for almost the entire model range, and the rise in prices ...
Electric vehicles: there are only a few hundred of them in Russia
The largest share (36.6%) falls on the Mitsubishi i-MiEV electric hatchback, of which 237 units are registered. Recall that the Japanese electric car on the Russian market will be sold officially, and therefore success is quite natural. In second and third place are Tesla Model S and Nissan Leaf, which sold almost the same circulation - 152 and 145 copies, ...
New Tesla: everything known details
Source: auto.mail.ru I want to drive a car: Pitfalls of new exercises on the autodrome ...
Provocateur - a new Russian car for 260,000 rubles
The project of an unusual city car (the so-called small cars for urban use) was developed by a designer from Moscow, Alexander Malyshev. Let's make it clear right away: this moment the machine, called the Mirrow Provocator, exists only ... in the form of computer sketches. But the participants of the ambitious startup are planning to show the first prototype this fall, and right away...
A hot crossover will appear under the Lada brand
If the Lada Vesta Sport Concept shown today is actually a pre-production version of the “hot” Vesta, then the XRAY Sport Concept is really just a concept, far from serial implementation. The recipe for creating the XRAY Sport version is similar to that used to prepare the 150-horsepower Vesta: lowered suspension, boosted to 150 ...
Maserati Ghibli special edition: even a hearse can be stylish
Italian bodywork studios are able to create not only stylish sports cars and cars, but also cars that do not seem to need a stylish appearance at all. Everyone has long been accustomed to the fact that the hearse must certainly be black and have a strict "timeless" design. But such a people are Italians: in last way their friends and relatives, the inhabitants of this ...
Bridge to the Crimea: construction began on the sea. Video
Prior to this, the construction of the facility was carried out only on land sections, according to the Crimean Bridge information center. Currently, at the western tip of Tuzla Island, piles are being driven under the supports that will raise the road part of the structure above the water. The foundation of each of them is formed from 12 tubular piles with a diameter of 1420 mm. Between...
Hybrid Mini Countryman: first official details
As stated in the official message of the brand, the development of a new "electrically charged" model is almost completed, and it will be equipped with two motors - an internal combustion engine simultaneously with an electric motor. The report also says that Mackensen and Wolf conducted a test drive of the brand's first hybrid model. From the published photos it can be seen that we are talking about a new modification of the Mini ...
You can treat them as you like - admire, hate, admire, feel disgust, but they will not leave anyone indifferent. Some of them are just a monument to human mediocrity, made of gold and rubies in life size, some are so exclusive that when...
The fastest cars in the world 2017-2018 model yearThe fastest cars in the world 2017-2018 model year
Fast cars are an example of the fact that automakers are constantly improving the systems of their cars and are periodically developing to create the perfect and fastest vehicle for movement. Many of the technologies that are developed to create a super fast car later go into mass production ...
The best gifts for car ownersThe best gifts for car owners
A car enthusiast is a person who spends a lot of time driving his car. Indeed, in order to ensure the necessary comfort in the car, as well as traffic safety, you need to make a lot of efforts when caring for a car. If you want to please your friend...
2017-2018: CASCO rating of insurance companiesEvery car owner strives to protect himself from emergencies related to road accidents or other damage to your vehicle. One of the options is the conclusion of a CASCO agreement. However, in an environment where there are dozens of companies providing insurance services in the insurance market, ...
The most expensive car in the worldThe most expensive car in the world
There is in the world great amount cars: beautiful and not so, expensive and cheap, powerful and weak, our own and others. However, there is only one most expensive car in the world - this is the Ferrari 250 GTO, it was produced in 1963 and only this car is considered ...
Which car is the most expensive jeep in the worldWhich car is the most expensive jeep in the world
All cars in the world can be divided into categories in which there will be an indispensable leader. So you can select the fastest, most powerful, economical car. There are a huge number of such classifications, but one is always of particular interest - the most expensive car in the world. In this article...
What cars are stolen most oftenWhat cars are stolen most often
Unfortunately, the number of stolen cars in Russia does not decrease over time, only the brands of stolen cars change. It is difficult to pinpoint a list of the most stolen cars, since each insurance company or statistical office has its own information. The exact data of the traffic police about what ...
Which car to choose a family manWhich car to choose a family man
A family car should be safe, roomy and comfortable. In addition, family cars should be easy to use. Varieties of family cars As a rule, most people associate the concept of "family car" with a 6-7-seat model. Universal. This model has 5 doors and 3...
Since the time of the first steam moving device Cagnoton, created in 1769, the automotive industry has stepped far forward. The variety of brands and models at the present time is amazing. Technical equipment and design will satisfy the needs of any customer. The purchase of a particular brand, the most accurate ...
- Discussion
- In contact with
› Why brakes anti-lock braking system (ABS)
Have you ever had to go around a sudden obstacle and brake at the same time? Surely yes. It would seem that this is difficult - he pressed the brake, turned the steering wheel and corrected the trajectory. However, everything is relatively simple up to a certain point. If at emergency braking press the brake pedal harder than necessary, the wheels may lock up and ...
There are two possible scenarios for the development of events. Both are due to the presence or absence of the anti-lock braking system ABS (ABS - Anti-lock Brake System). If the car is archaic, traces its pedigree from the mid-seventies of the last century or left the assembly line of one of the domestic automobile plants, then no matter how hard you turn the steering wheel, vehicle trajectory will not change. The fact is that the locked wheels, sliding, deprive the driver of the opportunity to maneuver - having fallen into the skid, the car will stupidly drive in a straight line, as if the steering wheel was cut off. Only an experienced pilot will be able to coolly unlock the wheels by momentarily releasing the brake pedal. And then, using impulse braking, regain control and extinguish speed. The second option is for a car equipped with ABS. The driver only needs to press the brake pedal harder and calmly work the steering wheel. Feel the difference?

For 30 years, the system has undergone major changes. The performance and the number of operation cycles per unit of time have increased tenfold. So, for example, the first control units for passenger cars weighed more than 7 kg. Modern ones are much more compact and pull a kilogram and a half.
Blocking is also dangerous because it can cause the car to skid or pull to the side. This can happen when there is a heterogeneous coating under the wheels, the axle load is greatly changed during the previous maneuver, or there are different tires (the latter sounds crazy, but, alas, it is not uncommon in Russia). In addition, with the wheels locked, the machine can change the trajectory under the influence of any lateral force (road slope or collision). Correcting the trajectory in this case is almost impossible.

ABS uses inductive frequency sensors and Hall effect sensors to determine rotation speed. Each new generation of wheel speed sensors is getting smaller, more accurate and more reliable. At first, only one sensor was installed, which was mounted on the rear axle gearbox or gearbox. Later, two more were added to it - on the front wheels. And only in latest versions ABS provides for the installation of sensors on each wheel, respectively, with individual modulators. By the way, the most ancient and primitive single-channel ABS acted immediately on all brake mechanisms.
Another negative effect of blocking is an increase in stopping distance. The point here is that the static friction force is usually greater than the sliding friction force. Therefore, in order to stop the car as quickly as possible, it is necessary to generate such a pressure in the brake lines that the wheels rotate on the verge of blocking during braking. There is such an important indicator as relative slippage. Depending on the degree of wheel inhibition, it can vary from zero (the wheel rolls without slipping) to 100% (the wheel is completely blocked). It has been experimentally established that the maximum braking efficiency is achieved at 15-20% slippage - that is, in the case when the speed of rotation of the braked wheel is 15-20% lower than the speed of the freely rotating wheel at a constant speed of the machine. Looking ahead, let's say that the electronics during braking maintains exactly this value, periodically blocking and unlocking the wheels.
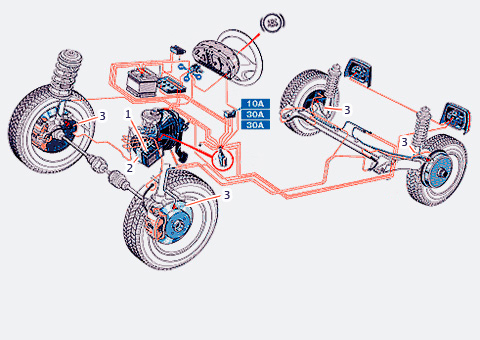
Almost any composition modern system ABS includes: an electronic control unit (1), a modulator (2) that changes the pressure in the hydraulic lines, wheel speed sensors (3) installed on the inside of the wheel hub.
Progressive humanity finally realized the harm of blocked wheels only in the 70s of the last century. The pioneer in this area was Mercedes-Benz, which, together with Bosch, developed a system that in 1979 began to be installed on Mercedes S-Class. The basic principle of the ABS was formed just then, and then only improved.

Modern electronics (ABS, traction control, ESP) take into account not only the speed of the wheels to keep the lateral and longitudinal dynamics of the car under control. Controlled are the angle of rotation of the steering wheel, the degree of body roll, acceleration ... The pressure in the brake circuits is generated from the totality of the received data, plus, in some cases, the engine thrust is forcibly changed.
The task of ABS is to regulate the speed of rotation of the wheels by changing the pressure in the lines of the brake system. To control the angular velocity, you need to know its magnitude and how it changes with time. Each wheel is equipped with a sensor that produces electrical impulses at a frequency proportional to the speed of rotation of the wheel. This information is sent to the ABS control unit.
If, during braking, the angular velocity of the wheel approaches zero, the electronic brain will immediately decide to “brake” it. The hydraulic modulator, using an electrovalve, relieves pressure from the line and redirects the "excess" portion of the brake fluid to the accumulator. The pressure will decrease until the wheel, again “grabbing” the coating, spins up to a certain speed. Further, ABS will again sharply increase the pressure in the line and slow down the wheel. The cycle will continue until the car comes to a stop or the driver releases pressure on the pedal to a point where ABS is not needed.
The systems available on the market are extremely fine-tuned and provide maximum braking performance.
Many will say: “Little wisdom!” You can intermittently brake yourself. And it's true: in many cases, this method of deceleration on vehicles not equipped with ABS allows you to avoid a sudden obstacle during emergency braking. When the wheels are blocked - you brake, as soon as they are "released" - you get the opportunity to correct the direction of movement. Naturally, in this scenario, the braking distance will increase significantly, but the driver will be able to go around the obstacle and extinguish the skid with a proactive steering action.
But, unfortunately, not a single titled racer is able to provide "portioned" braking with the frequency with which ABS does it. The system (depending on the version) manages to lock-unlock the wheels about 15 times per second. In addition, the driver simultaneously acts on all the brakes (this is how the first ABS systems worked), while modern 4-channel anti-lock systems monitor the speed of rotation and regulate the braking force for each wheel separately.
Hydraulic modulator combined with control box (black).
In most modern cars, ABS works in conjunction with EBD (Electronic Brake Distribution) - a brake force distribution system that doses the braking intensity for each wheel. With EBD, you can safely brake in a turn and in a “mixed”. The electronics, by the difference in rotational speeds, will understand that the wheels have fallen into areas with a heterogeneous surface, and will reduce the braking forces on the wheels that have better grip. By the way, the intensity of deceleration in this case will decrease and will be determined by the friction force of the wheel (s), which has the worst grip.
It is worth noting that for maximum deceleration efficiency, the brake pedal on cars with ABS must be pressed to the floor with all your strength. However, the latter is not necessary for those drivers whose cars are equipped with the Brake Assist system, which itself creates excess pressure in the brake line, “braking” for a weak or indecisive person. With regular decelerations, it does not interfere. However, a sharp press (blow) on the Brake Assist pedal is regarded as a signal for emergency braking and takes effect.
But not everything is so smooth. ABS, like any other system, has disadvantages. For example, a simple "anti-block" can lose to conventional brakes on snow, ice or sand, negating the advantages of studded tires. Indeed, on ice, spikes provide the greatest deceleration only at maximum relative slippage, when they dig into the ice like claws and furrow it. The trick is that ABS, trying to brake the wheels, does not allow the spikes to work and thereby increases the braking distance. The same thing happens on dirt roads (sand, gravel, clay) and snow-covered surfaces.

The presence of ABS is not a reason to refuse studded tires. During lockup, the studs will still cling to the ice and provide more reliable deceleration than non-studded tires.
Cars with ABS in this case have a longer braking distance, because the constantly unlocking wheels do not create a “plough effect”. But it is on such surfaces that the blocked wheels have maximum braking efficiency - due to the fact that “rollers” of soil or snow are raked in front of them. That's why you need to remember: on an icy, snowy or unpaved surface, the braking distance of a car not equipped with ABS can be shorter.
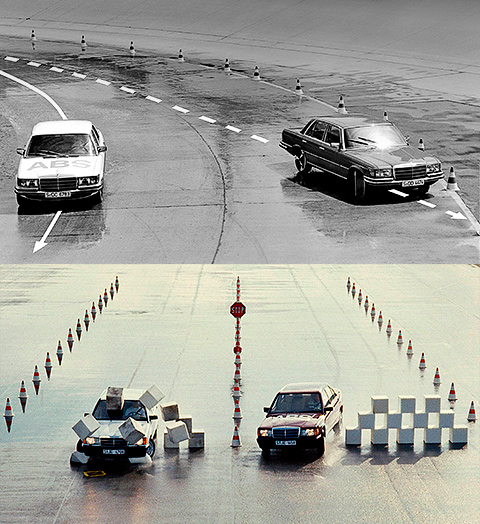

Vehicles with ABS remain steerable during emergency braking.
Enclose a small pig ABS can and on a rough road. If, during braking, one wheel hangs in the air for a moment and locks up, the deceived electronics will begin to save you from skidding and immediately reduce the pressure in the remaining highways. In a turn, the car will wag its tail unpleasantly, and the braking distance will increase. In principle, no one is immune from such accidental breaks, but you need to remember that the key to adequate ABS operation is a good suspension.
If there is any malfunction in the system, the control lamp lights up on the instrument panel. In this case, there is only one advice - run to the service.
Progress gives birth to ever more advanced systems. Operating with a large number of indications, they are able to adapt to the type of road surface and brake according to one of the pre-established effective algorithms. Of course, electronics cannot be taken as a panacea for all ills, but the statistics are stubborn things: a well-tuned ABS with all the car's systems working on dry and wet surfaces on average helps to save up to 20% of the braking distance and leaves the driver a chance to maneuver. Needless to say, life and health may depend on these precious meters?
During rectilinear movement during the braking of the car, it is affected by different forces: vehicle weight, braking force and lateral force. The magnitude of the forces depends on many factors, such as the speed of the vehicle, the size of the wheels, the condition and design of the tires and the roadway, the design of the brake system and its technical condition.
Rice. Forces acting on the wheel during braking:
G is the weight of the car; FB - braking force; FS - lateral force; νF is the vehicle speed; α is the slip angle; ω - angular velocity
During rectilinear movement of the vehicle at a constant speed, there is no difference in the speeds of rotation of the wheels. In this case, there is also no difference between the reduced speed of the vehicle νF and the average speed of rotation of the wheels νR consistent with it, i.e. νF = νR. Under the average speed of rotation of the wheels is understood the value
νR = (νR1+ νR2 + νR3 + νR4)/4,
where νR1…νR4 are the rotation speeds of each wheel separately.
But as soon as the process of intensive braking begins, the reduced speed of the car νF begins to exceed the average speed νR of wheel rotation, since the body "overtakes" the wheels under the influence of the inertia force of the car's mass, i.e. νF>νR.
In such a situation, a phenomenon of uniform moderate slip occurs between the wheels and the road. This slip is the operating parameter of the brake system and is defined as:
λ = (νF - νR) / νF 100%
Physically, working sliding, unlike emergency skidding, is realized due to the deflection of the wheel tire tread, the shift of fine fractions on the road surface, and due to the depreciation of the automobile suspension. These factors keep the vehicle from skidding and display useful essence working slip of the wheel during its braking. It is clear that in this case, the deceleration of the rotation of the wheel occurs gradually and in a controlled manner, and not instantly, as in the case of blocking.
The value of λ is called the slip coefficient and is measured as a percentage. If λ = 0%, then the wheels rotate freely, without being affected by road friction resistance. The slip coefficient λ = 100% corresponds to the skidding of the wheel when it enters the locked state. At the same time, braking efficiency, stability and controllability of the car during braking are significantly reduced.
When the effect of the working slip appears, in which the normal rolling of the wheels still takes place between them and the road, a uniformly increasing friction resistance arises, expressed by the adhesion coefficient in the direction of movement μHF, which is a function of the working slip γ and creates the braking force of the vehicle FB = K μHFG. K - constructive coefficient of proportionality, depending on the state of the tire tread, brake pads, brake discs and brake calipers.
The figure shows the dependence of the relative slip of the wheel on the friction coefficient in the direction of motion μHF and the coefficient of adhesion in the transverse direction μS when braking on dry concrete pavement.

Rice. The dependence of the coefficient of adhesion on the slip of the wheels.
As can be seen from the figure, the value of the relative slip of the wheel λ reaches its maximum value at certain values of the friction coefficient in the direction of motion μHF, with a decrease in the coefficient of adhesion in the transverse direction μS. For most road surfaces, at values of γ, and hence the braking force, in the range from 10% to 30%, μHF reaches its maximum value and this value is called critical (λ)kp. Within these limits, the coefficient of adhesion in the transverse direction μS has enough high value, which ensures the stable movement of the car when braking, if a lateral force acts on the car.
The shape of the curves of the coefficient of friction in the direction of travel μHF, and the coefficient of friction in the transverse direction μS depends to a large extent on the type and condition of the road surface and tires.
It is important to note that for small γ (from 0% to 7%) the braking force depends linearly on slip.
During emergency braking, a significant effort on the brake pedal can cause the wheels to lock. At the same time, the grip strength of the tires with the road surface is sharply weakened, and the driver loses control of the car.
Appointment and device ABS
Anti-lock systems(ABS) brakes are designed to provide constant monitoring of the grip force of the wheels with the road and adjust accordingly in each this moment braking force applied to each wheel. ABS redistributes pressure in the branches of the wheel brake hydraulic drive in such a way as to prevent wheel blocking and at the same time achieve maximum braking force without losing vehicle controllability.
The main task of the ABS is to maintain the relative slip of the wheels in the process of braking within narrow limits near λkp. In this case, optimal braking performance is ensured. For this purpose, it is necessary to automatically adjust the braking torque supplied to the wheels during braking.
Many different ABS designs have appeared that solve the problem of automatic control of the braking torque. Regardless of the design, any ABS should include the following elements:
- sensors, the function of which is to issue information, depending on the adopted control system, about the angular velocity of the wheel, the pressure of the working fluid in the brake drive, vehicle deceleration, etc.
- control unit, usually electronic, which receives information from sensors, which, after logical processing of the information received, gives a command to the actuators
- actuators (pressure modulators), which, depending on the command received from the control unit, reduce, increase or maintain a constant pressure in the brake drive of the wheels

Rice. ABS control scheme:
1 - actuator; 2 - the main brake cylinder; 3 – wheel brake cylinder; 4 - control unit; 5 - wheel speed sensor
The process of regulation with the help of ABS wheel braking is cyclic. This is due to the inertia of the wheel itself, the drive, as well as the ABS elements. The quality of regulation is assessed by how much the ABS ensures the sliding of the braking wheel within the specified limits. With a large range of cyclic pressure fluctuations, comfort is disturbed during braking "twitching", and the elements of the car experience additional loads. The quality of the ABS operation depends on the adopted regulation principle, as well as on the speed of the system as a whole. The speed determines the cyclic frequency of change of the braking torque. An important property ABS should be able to adapt to changing braking conditions (adaptiveness) and, first of all, to changing the friction coefficient during braking.
Developed big number principles (functioning algorithms) according to which the ABS operates. They differ in complexity, cost of implementation and in the degree of satisfaction of the requirements. Among them, the most widely used is the operation algorithm for decelerating the braking wheel.
The braking dynamics of a car with ABS depends on the adopted scheme for installing the elements of this system. From the point of view of braking efficiency, the scheme with independent regulation of each wheel is the best. To do this, it is necessary to install a sensor on each wheel, and in the brake actuator - a pressure modulator and a control unit. This scheme is the most complex and expensive.
There are simpler ABS schemes. Figure b shows the ABS diagram with controlled braking of the two rear wheels. For this, two wheel speed sensors and one control unit are used. In such a scheme, the so-called low- or high-threshold regulation is used. Low-threshold regulation provides for the control of a braking wheel that is in the worst grip conditions (“weak” wheel). In this case, the braking capabilities of the "strong" wheel are underused, but equal braking forces are created, which helps to maintain directional stability during braking with a slight decrease in braking efficiency. High-threshold regulation, i.e. steering the wheel in the best traction conditions, gives higher braking efficiency, although stability is somewhat reduced. "Weak" wheel with this method of regulation is cyclically blocked.
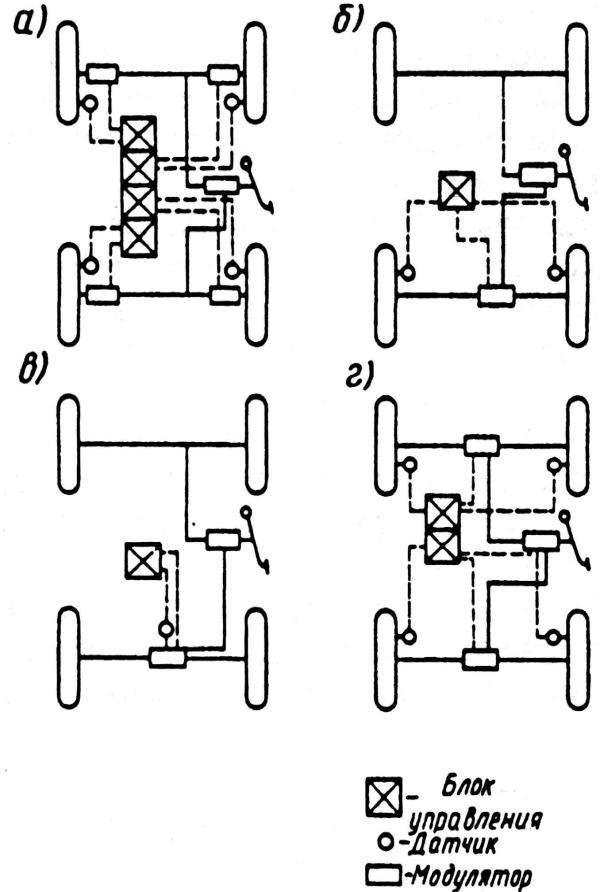
Rice. ABS installation diagrams on a car
Even more simple circuit shown in figure c. It uses one angular velocity sensor located on the cardan shaft, one pressure modulator and one control unit. Compared to the previous one, this circuit has a lower sensitivity.
Figure d shows a diagram in which angular velocity sensors are used on each wheel, two modulators, two control units. In such a scheme, both low- and high-threshold regulation can be used. Often in such schemes, mixed regulation is used (for example, low threshold for the wheels of the front axle and high threshold for the wheels of the rear axle). In terms of complexity and cost, this scheme occupies an intermediate position between those considered.
The ABS operation can take place in a two- or three-phase cycle.
With a two-phase cycle:
- second phase - depressurization
With a three-phase cycle:
- the first phase is the increase in pressure
- second phase - depressurization
- the third phase - maintaining the pressure at a constant level
When installed on an ABS passenger car, closed and open hydraulic brake actuators are possible.
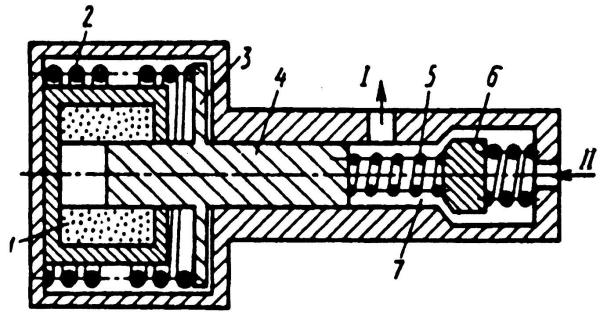
Rice. Diagram of the hydrostatic brake pressure modulator
A closed or closed (hydrostatic) drive works on the principle of changing the volume of the brake system during braking. Such a drive differs from the usual one by installing a pressure modulator with an additional chamber. The modulator operates on a two-phase cycle:
- The first phase - the pressure build-up, the winding of the electromagnet 1 is disconnected from the current source. Anchor 3 with plunger 4 is under the action of spring 2 in the extreme right position. Valve 6 is pressed from its seat by spring 5. When you press the brake pedal, the fluid pressure generated in the master cylinder (pin II) is transmitted through pin I to the working brake cylinders. The braking torque increases.
- The second phase is pressure release: the control unit connects the winding of electromagnet 1 to the power source. Armature 3 with plunger 4 moves to the left, while increasing the volume of chamber 7. At the same time, valve 6 also moves to the left, blocking output I to the working brake cylinders of the wheels. Due to the increase in the volume of chamber 7, the pressure in the working cylinders drops, and the braking torque decreases. Next, the control unit gives a command to increase the pressure, and the cycle repeats.
An open or open hydraulic brake actuator (high pressure actuator) has an external source of energy in the form of a high pressure hydraulic pump, usually in combination with a hydraulic accumulator.
At present, preference is given to a high-pressure hydraulic drive, which is more complex than a hydrostatic drive, but has the necessary speed.

Rice. Dual circuit brake actuator with ABS:
1 – wheel sensor of angular speed; 2 - modulators; 3 - control units; 4 - hydraulic accumulators; 5 - check valves; 6 - control valve; 7 - high pressure hydraulic pump; 8 - drain tank
The brake drive has two circuits, so it is necessary to install two independent hydraulic accumulators. The pressure in the accumulators is maintained at the level of 14…15 MPa. A two-section control valve is used here, which provides a follow-up action, i.e. proportionality between the force on the brake pedal and the pressure in the brake system. When you press the brake pedal, the pressure from the hydraulic accumulators is transmitted to the modulators 2, which are automatically controlled by the electronic units 3, which receive information from the wheel sensors 1. The figure shows a diagram of a two-phase spool pressure modulator for a high-pressure hydraulic brake drive. Consider the phases of this modulator:
- Pressure build-up phase 1: The ABS control unit disconnects the solenoid coil from the power source. The spool and armature of the solenoid are moved to the upper position by the force of the spring. When the brake pedal is pressed, the control valve communicates the accumulator (terminal I) with the discharge channel of the pressure modulator. Brake fluid under pressure flows through outlet II to the working cylinders of the brake mechanisms. The braking torque increases.
- Phase 2 depressurization: the control unit communicates the solenoid coil with the power supply. The solenoid armature moves the spool to the down position. The supply of brake fluid to the working cylinders is interrupted: output II of the working brake cylinders communicates with drain channel III. The braking torque is reduced. The control unit gives a command to increase the pressure by disconnecting the solenoid coil from the power source, and the cycle repeats.
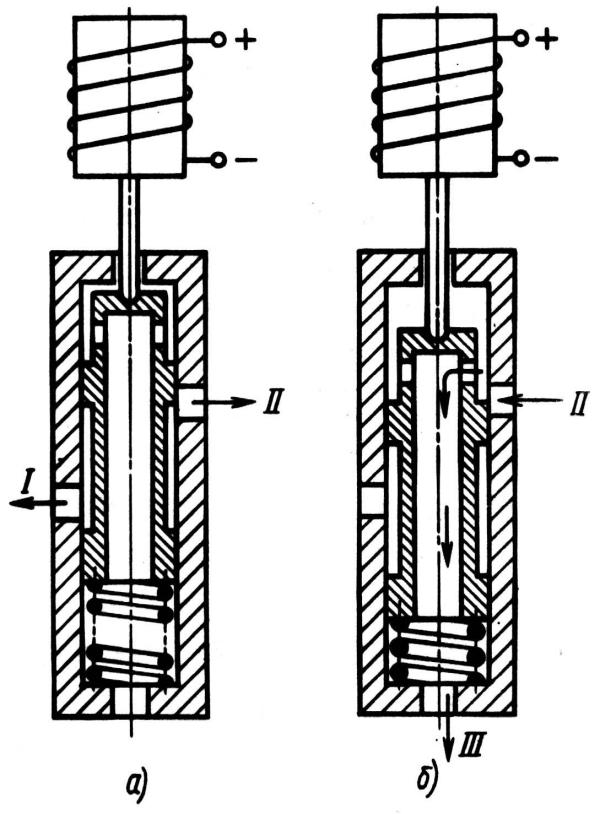
Rice. Scheme of operation of a two-phase high pressure modulator:
a – phase 1; b - phase 2
Currently, ABS operating on a three-phase cycle is more common. An example of such a system is the fairly common Bosch 2S ABS system.
This system is built in as an additional to the usual brake system. Between the main brake cylinder and the wheel cylinders, pressure (H) and unloading (P) solenoid valves are installed, which either maintain a constant level or reduce the pressure in the wheel drives or in the circuits. The solenoid valves are actuated by a control unit that processes information from four wheel sensors.
The control unit, which continuously receives data on the speed of rotation of each wheel and its changes, determines the moment of blocking, then, if necessary, releases pressure, turns on the hydraulic pump, which returns part of the brake fluid back to the master cylinder supply tank.
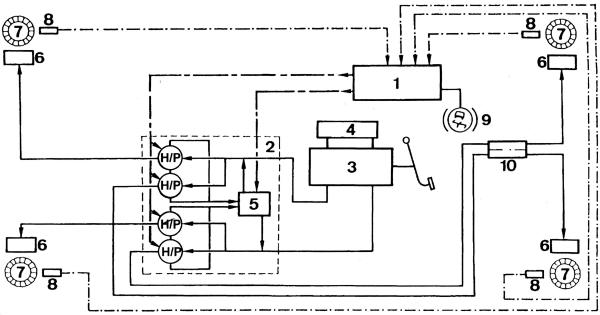
Rice. Functional diagram of ABS Bosch 2S:
1 - control unit; 2 - modulator; 3 – the main brake cylinder; 4 - tank; 5 - electrohydraulic pump; 6 - wheel cylinder; 7 – wheel sensor rotor; 8 – wheel inductive sensor; 9 - signal lamp; 10 - brake force regulator; Н/Р – delivery and unloading solenoid valves; — .-. BU input signals; - - - - CU output signals; –––– brake pipeline
The ABS modulator contains solenoid valves, a hydraulic pump with fluid pressure accumulators, a solenoid valve relay and a hydraulic pump relay.

Rice. Electro-hydraulic modulator:
1 - electromagnetic valves; 2 - hydraulic pump relay; 3 - relay of electromagnetic valves; 4 - electrical connector; 5 – hydraulic pump electric motor; 6 - radial piston element of the pump; 7 - pressure accumulator; 8 - silencer
The system operates according to a program divided into three phases: 1 - normal or normal braking; 2 - keeping the pressure at a constant level; 3 - pressure relief.
Normal braking phase
During normal braking, there is no voltage on the solenoid valves, from the master cylinder the brake fluid under pressure flows freely through the open solenoid valves and actuates the wheel brakes. The hydraulic pump is not working.

Rice. Deceleration phases:
a) the phase of normal braking; b) the phase of holding the pressure at a constant level; c) depressurization phase; 1 – wheel sensor rotor; 2 - wheel sensor; 3 - wheel (working) cylinder; 4 – electrohydraulic modulator; 5 - solenoid valve; 6 - pressure accumulator; 7 - pressure pump; 8 - the main brake cylinder; 9 - control unit
Pressure holding phase
When signs of blocking of one of the wheels appear, the control unit, having received the appropriate signal from the wheel sensor, proceeds to the execution of the cycle program for maintaining pressure at a constant level by disconnecting the main and corresponding wheel cylinder. A current of 2 A is applied to the solenoid valve coil. The valve piston moves and blocks the flow of brake fluid from the master cylinder. The pressure in the working cylinder of the wheel remains unchanged, even if the driver continues to press the brake pedal.
Release phase
If the risk of wheel blocking persists, the control unit supplies a larger current to the solenoid valve winding: 5 A. As a result of additional movement of the valve piston, a channel opens through which the brake fluid is discharged into the fluid pressure accumulator. The pressure in the wheel cylinder drops. The control unit issues a command to turn on the hydraulic pump, which removes part of the fluid from the pressure accumulator. The brake pedal rises, which is felt by the beating of the brake pedal.
The inductive wheel sensor consists of a winding 5 and a core 4. The gear wheel 6 has a speed equal to the speed of the wheel. When the wheel 6, made of ferromagnetic iron, rotates, the magnetic flux changes depending on the passage of the teeth of the rotor, which leads to a change in the alternating voltage in the coil. The frequency of voltage changes depends on the speed of the gear wheel, i.e. the speed of the wheel of the car. The air gap and the size of the tooth have a great influence on the amplitude of the signal. This allows you to determine the position of the wheel by the intervals between the teeth within a half or a third. The signal from the inductive sensor is transmitted to the electronic control unit.

Rice. Inductive sensor:
1 – permanent magnet; 2 - body; 3 – sensor mount; 4 - core; 5 - winding; 6 - gear wheel
Inductive sensors can be mounted on the wheel drive shaft, on the bevel gear drive shaft for rear-wheel drive vehicle models, on the pivot pins and inside the wheel hub.
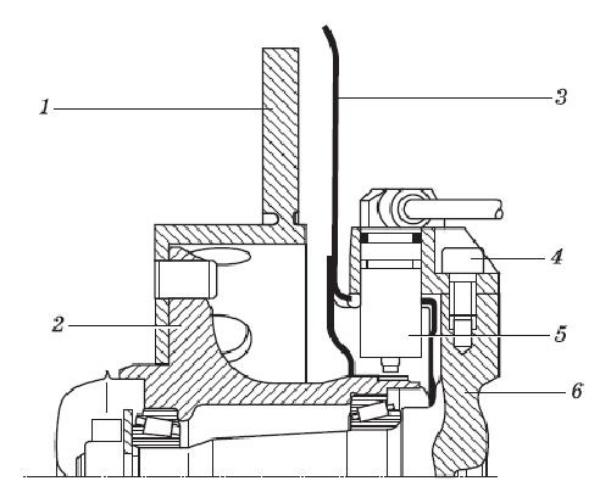
Rice. Mounting the inductive sensor on the stub axle:
1 - brake disc; 2 - front hub; 3 - protective cover; 4 - screw with internal hexagonal engagement; 5 – sensor; 6 - pivot pin

Rice. Mounting the inductive sensor inside the wheel hub:
1 – wheel mounting flange; 2 - balls; 3 - ring ABS sensor; 4 – sensor; 5 - flange mounting to the suspension.
More advanced are active sensors used to measure wheel speed. The sensitive element of the electronic cell 2 of such a sensor is made of a material whose electrical conductivity depends on the strength of the magnetic field. When the drive disk 3 rotates, the magnetic field changes. Caused by the changing magnetic field fluctuations of the current passing through the sensitive element are converted in the electronic circuit into voltage fluctuations output to the external contacts of the sensor. When the master disk rotates, a sensor installed near it generates rectangular pulses, the frequency of which corresponds to the frequency of rotation of the disk. The advantage of this sensor compared to previously used systems is the accurate registration of the speed when it decreases until the wheel stops.
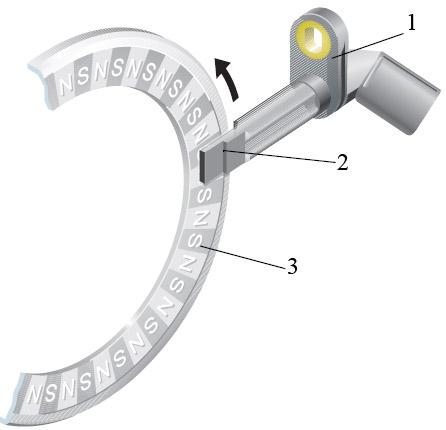
Rice. Active sensor:
1 – sensor body; 2 – electronic cell of the sensor; 3 - setting disk
As a rule, there should be a control light on the instrument panel, which should go out when the engine is running or if the vehicle speed exceeds 5 km / h. It will also come on if one of the wheels spins for more than 20 seconds or if the electrical supply is less than 10 volts. The system indicator light warns the driver that a system malfunction has caused a system malfunction. automatic shutdown however, the braking system continues to function as a normal non-ABS braking system.
A similar principle of operation is used for Bosch ABS 2E, however, this system uses a balancing cylinder to equalize the pressure in the rear wheel brake drive, which allows three valves to be used instead of four solenoid valves. Thus, the modulator consists of not four, but three solenoid valves, an equalizing cylinder, a two-piston pressure hydraulic pump, two pressure accumulators, a pump relay and a solenoid valve relay.
The system works as follows. During normal braking, brake fluid under pressure from the master cylinder enters the working cylinders of both front wheels and the right rear wheel through three solenoid valves, which are normally closed. The brake fluid is supplied to the working cylinder of the left rear wheel through the open bypass valve of the balancing cylinder. When there is a danger of blocking one of the front wheels, the control unit issues a command to close the corresponding solenoid valve, preventing the increase in pressure in the wheel cylinder. If the risk of blocking the wheel has not been eliminated, current is supplied to the solenoid valve, which ensures the opening of the section of the line between the working cylinder of the wheel and the pressure accumulator. The pressure in the brake drive drops, after which the control unit issues a command to turn on the hydraulic pump, which distills the fluid into the main cylinder through the equalizing cylinder.
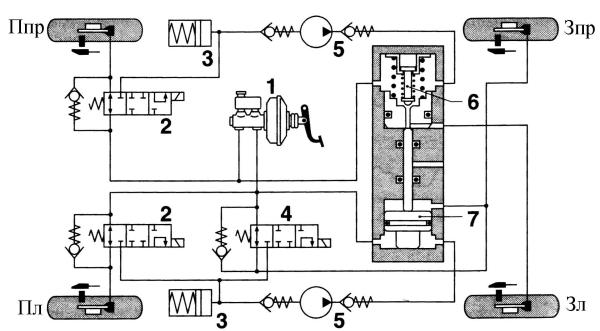
Rice. ABS 2E by Bosch in the normal braking phase:
1 - the main brake cylinder; 2 - solenoid valve; 3 – pressure accumulator; 4 - solenoid valve of the rear axle; 5 - pressure pump; 6 - bypass valve; 7 – equalizing cylinder piston; Ppr - front right wheel; Pl - front left wheel; Zpr - rear right wheel; Zl - rear left wheel
When there is a danger of one of the rear wheels locking up, the pressure will be adjusted in both rear brakes at the same time in order to prevent the rear wheels from skidding.
The solenoid valve for the right rear brake drive is set to the position of holding constant pressure and blocks the section of the line between the master cylinder and the wheel cylinder. Pressure of various magnitudes begins to act on the opposite end surfaces of the piston 7 of the equalizing cylinder, as a result of which the piston with the rod moves in the direction of the least pressure (up in the figure) and closes valve 6, disconnecting the main cylinder and the wheel cylinder of the left rear brake. The piston of the equalizing cylinder, due to the resulting pressure difference in the working cavities above and below it, is always set to a position at which the pressure in the drives of both rear brakes is the same.
If the risk of blocking the rear wheels remains, the VU energizes the solenoid valve in the rear wheel circuit with a current of 5 A. The solenoid valve spool moves and opens the section of the circuit between the right rear brake working cylinder and the fluid pressure accumulator. The pressure in the circuit decreases. The hydraulic pump pumps brake fluid into the master cylinder through the balance cylinder. As a result of a decrease in pressure in the space above the piston 7, its next movement occurs, the spring of the central valve is compressed, and the volume of space under the upper piston increases. The pressure in the left wheel brake cylinder is reduced. The piston of the equalizing cylinder is again set to the position corresponding to the equality of pressures in the drives of both rear brakes. After the threat of blocking the wheels is eliminated, the solenoid valve returns to its original position. The piston of the equalizing cylinder under the action of the spring also occupies the initial lower position.
More advanced is the Bosch 5 series ABS with block 10, which belongs to a new generation of ABS systems, representing a closed hydraulic system that does not have a channel for returning brake fluid to the reservoir that feeds the master brake cylinder. The scheme of this system is shown on the example of the Volvo S40.
Rice. ABS diagram of the 5th Bosch series:
1 - check valves; 2 - plunger pump valve; 3 - hydraulic accumulator; 4 – pulsation suppression chamber in the system; 5 – electric motor with eccentric plunger pump; 6 - reservoir for brake fluid; 7– service brake pedal; 8 - amplifier; 9 - the main brake cylinder; 10 - block ABS; 11 - exhaust controlled valves; 12 - inlet controlled valves; 13 - throttling valve; 14-17 - brake mechanisms
The electronic and hydraulic components are mounted as a single unit. These include, in addition to those indicated in the diagram: a relay for turning on the electric motor of the plunger pump 5 and a relay for turning on the inlet 12 and outlet 11 valves. The external components are: the ABS operation warning light in the instrument panel, which lights up in the event of a malfunction in the system, as well as when the ignition is turned on for four seconds; brake light switch and wheel speed sensors. The unit has an output to the diagnostic connector.
The throttle valve 13 is installed to reduce the braking force on the rear wheels in order to avoid their blocking. Due to the fact that the brake system has a setting for a “weaker” rear wheel (this means that the rear wheel brake pressure is the same, and its value is set for the wheel closest to blocking), a throttling valve is installed one per circuit.
Brakes 14-17 include brake discs and single-piston floating caliper calipers with brake pads equipped with friction lining wear control calipers. The brake mechanisms of the rear wheels are similar to the front ones, but they have solid brake discs (ventilated on the front ones) and a parking brake actuator mounted in the caliper.
When the brake pedal 7 is pressed, its lever releases the brake light switch button, which, when actuated, turns on the brake lights and puts the ABS on standby. The movement of the pedal through the rod and the vacuum booster 8 is transmitted to the pistons of the main cylinder 9. The central valve in the secondary piston and the cuff of the primary piston block the communication of the circuits with the reservoir 6 for brake fluid. This leads to an increase in pressure in the brake circuits. It acts on the pistons of the brake cylinders in the brake calipers. As a result, the brake pads are pressed against the discs. When the pedal is released, all parts return to their original position.
If, during braking, one of the wheels is close to blocking (as reported by the speed sensor), the control unit closes the intake valve 12 of the corresponding circuit, which prevents a further increase in pressure in the circuit, regardless of the increase in pressure in the main cylinder. At the same time, the hydraulic plunger pump 5 starts to work. If the rotation of the wheel continues to slow down, the control unit opens the outlet valve 11, allowing the brake fluid to return to the hydraulic accumulators 3. This reduces the pressure in the circuit and allows the wheel to rotate faster. If the rotation of the wheel is excessively accelerated (compared to other wheels), to increase the pressure in the circuit, the control unit closes the exhaust valve 11 and opens the inlet valve 12. Brake fluid is supplied from the main brake cylinder and using the plunger pump 5 from the hydraulic accumulators 3. The damper chambers 4 smooth ( suppress) pulsations that occur in the system during the operation of the plunger pump.
The brake light switch informs the control module of braking. This allows the control module to more accurately control wheel rotation parameters.
The diagnostic connector is used to connect the Volvo System Tester when performing diagnostics.
If the vehicle is equipped with DSA (Dynamic Stability Control), the DSA control module receives the wheel speed data needed to measure wheel spin. The DSA system control module receives this information from the ABS system control module. Three communication lines serve this purpose. The DSA system does not use the brakes to control slip.
Internal relays (for pump and valves) have separate connections protected by fuses.
When the ignition is switched on, the system checks electrical resistance all components. During this test, the warning light is on. After completion of the test (4 s), the lamp should go out.
» What is ABS (ABS) - anti-lock braking system
What is ABS- Many of us ask this question when choosing a new or used foreign car, specifying its characteristics and list of options. AT modern world it is difficult to imagine a car that does not include an anti-lock braking system (abbreviated as ABS or ABS). Its task is to prevent the wheels from locking during braking. This allows you to improve the stability and controllability of the car on the road, as well as reduce the braking distance of the car.
Most situations on the road do not require something complicated from the driver - just slow down. However, each of us got into such moments when it is simply necessary to resort to emergency braking, which increases the chance of getting into an accident dozens of times. When driving a car that is not equipped with ABS, if you press the accelerator pedal hard, you can easily lose control. Traction is lost due to the wheels locking and sliding, and the car goes into a skid, like a skater on skates.
Many experienced drivers will say that you can use the impulse method or just intermittently apply the brake, but will they remember this in a critical and emergency situation and will they have time to take the right decision in a split second without the help of ABS? What can we say about an ordinary driver or a beginner - for them, the anti-lock brake system and its role in the operation of the car is extremely important.
A Brief History of the ABS System
For the first time, the problem of wheel locking during braking became relevant in the operation of railway transport. The blocked train wheels not only wore out faster, but could also bring to great tragedy- derailment of the train. In 1936, Bosch patented a technology to prevent wheel lock, but it was impossible to implement it due to the small development of electronics. Real progress awaited this area in the 60-70s of the last century, when semiconductor technologies appeared. As a result, in 1970 the largest German automaker Daimler-Benz presented the first models of safe ABS. A little later, after 8 years, the first car equipped with an ABS system appeared. They became the Mercedes-Benz S-class.
What is ABS. The device and principle of operation of the system
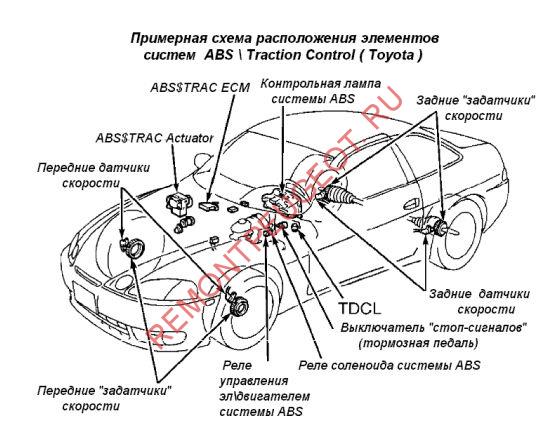
The ABS system includes the following elements:
- ABS sensor (in another way it is also called a speed, rotation or acceleration sensor);
- ABS electronic control unit (ECU);
- Hydraulic block and ABS valves;
- Brake mechanisms ABS systems.
How does the ABS system work?
- Anti-lock brake system works quite interesting. By pressing the brake pedal, a certain pressure is formed in the hydraulic brake system. This allows you to press the pads to the brake discs through the calipers, and due to this, stop the car.
- abs sensor, most often installed on each front wheel and on the rear axle (three-channel type), plays the role of "eyes and ears" of the entire anti-lock braking system, in the event of a blockage, signaling the ECU to reduce the brake fluid pressure. As soon as the speed sensor detects that the wheel is spinning again, it sends information to the ABS about the restoration of the previous pressure in the brake line.
- ABS valve body in most cars, it is located near the ECU or combined and consists of several valves that control the pressure of the brake fluid. All these valves are placed close to each other and closed by a solid body.
If during the braking process the wheel tries to slip, then the ECU, using the valves of the ABS hydraulic unit, reduces or completely limits the flow of fluid to the brake cylinder. If this is not enough, then the solenoid valve will send the brake fluid to the outlet part, reducing the pressure. As soon as the wheel regains the speed of the rest, the ABS computer sends information about the need to open the valves, and the ABS brake mechanism again feels the same pressure.
And so the wheels continue to lock and unlock, creating an impulse braking effect, allowing you to shorten the braking distance and keep the car stable on the road. What is another advantage of the modern ABS system is the ability of the rotation sensors to respond to even the slightest change in the speed of each particular wheel. The ABS control unit works quickly and instantly understands that it is time to reduce the braking effect, since it is able to receive from 6 to 20 signals from speed sensors per second. As a result, the wheel does not even have time to lock up, and its number of revolutions is adjusted by the ABS “on the go”.
How to understand if the ABS system is working and what to do if it is turned on?
You can find out about the operation of the ABS system by lighting up. It is usually red or yellow color and consists of the corresponding inscription. In addition, a jolt or vibration will be felt through the brake pedal along with a sound effect. The reason for this is the process of constantly opening / closing valves that regulate the pressure on the brakes.
If you feel a vibration in the pedal, do not remove your foot and continue to apply a lot of effort. On vehicles with ABS hard braking it is best to immediately squeeze out the brake and clutch pedals to the stop. Thanks to this, you will completely stop braking the engine, improving the effectiveness of the ABS. Don't try to understand, eliminate or react to inhibitory pulsations. The task of the driver is to quickly and with decent force press the brake pedal to the floor and do not remove his foot from it until the vehicle comes to a complete stop.
By the way, if, when the ignition is turned on, it does not light up along with the control devices, then this may indicate a malfunction in this system. Quite often, the problem is that after replacing the racks or other serious things, the abs sensor fails, or inattentive service specialists simply forget to connect it. Often ABS sensor it just gets very dirty due to its location near rotating parts and wheels, so a simple cleaning of the contacts "brings it back to life."
What are the benefits of an anti-lock brake system?
We list just a few of the main positive aspects in the operation of the ABS system:
- Ensures the safety of the driver and his passengers;
- Reduces braking distance on various road surfaces;
- It does not allow blocking of the drive wheels, which means that it allows the driver to maneuver, for example, to go around an obstacle or maintain control on a sharp turn;
- Reduces the chance of getting into an uncontrolled skid;
- Promotes even tire tread wear.
Video about the ABS system
As a conclusion
What is ABS in a modern car? This is a reliable and functional option that contributes to the safety of the driver and his passengers. The ABS system is included in the initial package of many even budget cars. Today, the anti-lock braking system is as integral and indispensable as the traditional elements of a car - the engine, steering wheel, tires, gearbox, and more. etc. Despite the usefulness of the ABS system, you should not rely entirely on electronics. Try to avoid cases of sudden braking, in which the anti-lock braking system is activated. Remember that keeping the distance several times reduces the chances of getting into an accident. Safe roads to you!
 Brake system of the car - repair or replacement
Brake system of the car - repair or replacement
 Electronic systems car - to help the driver
Errors Peugeot 308, 408, 3008 Peugeot 307 sensors What start-stop system?
Checking the brakes - checking the brake fluid, pedal and handbrake
Electronic systems car - to help the driver
Errors Peugeot 308, 408, 3008 Peugeot 307 sensors What start-stop system?
Checking the brakes - checking the brake fluid, pedal and handbrake
In the past few years, equipping cars with an anti-lock system or simply ABS has become fashionable among eminent manufacturers. According to various sources, about two-thirds of all cars produced today are equipped with ABS, there is a tendency for this technology to break through even in inexpensive basic versions of cars.
ABS (ABS) system
Why did manufacturers decide to put something outlandish on most of the produced cars until recently, and what benefits does such a technological seasoning give to your car?
When did the anti-lock braking system appear?
ABS was first tested in 1920 on aircraft landing gear. In aviation and today each aircraft is equipped with a number of braking systems, among which there is anti-lock braking.
The first workable version of the anti-lock braking system in road transport was tested by the German concern Daimler-Benz. A giant stepped on his heels engineering Bosch. Anti-lock braking systems, which first began to be installed serially on the Mercedes S-Class and BMW 7 Series in 1978, were jointly developed by these corporations.
Since 2004, ABS has been fitted as standard on all European vehicles.
What is ABS for and how to drive with it?
The anti-lock braking system of a car is a kind of addition to the brakes of your car. During hard braking, ABS helps to maintain stability and brake faster, because the system does not allow the pads to completely press the brake disc. Thus, blocking of the wheel during braking is not allowed, and the chances of letting the car go into an uncontrolled skid are reduced.
ABS allows you to control on slippery roads - this is its main purpose. Also, the system will help the driver during hard braking. The presence of this system on board the car from the driver will not require any special driving skills. ABS makes life easier for drivers difficult situations. In normal driving situations, brake control is entirely up to the driver.
For an inexperienced driver, having an anti-lock braking system in a car is a great help in mastering all the intricacies of driving. A person with a long driving experience can independently control the moment when the wheels begin to block, while weakening the braking force. With the presence of ABS, you can simply press the brake pedal with maximum force - this will provide effective braking.

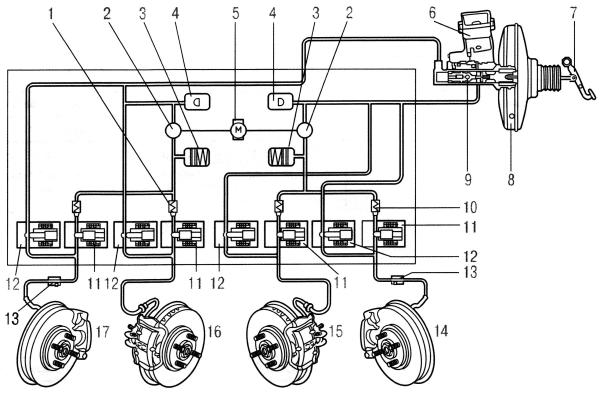
Anti-lock braking system device - diagram
- expansion tank
- vacuum brake booster
- brake pedal position sensor
- brake pressure sensor
- Control block
- return pump
- pressure accumulator
- damping chamber
- front left brake inlet valve
- front left brake actuator exhaust valve
- rear right brake inlet valve
- right rear brake actuator exhaust valve
- front right brake inlet valve
- front right brake actuator exhaust valve
- rear left brake inlet valve
- rear left brake actuator exhaust valve
- front left brake cylinder
- front left wheel speed sensor
- front right brake cylinder
- front right wheel speed sensor
- rear left brake cylinder
- rear left wheel speed sensor
- rear right brake cylinder
- rear right wheel speed sensor
How does this ABS work?
The device of the system is relatively simple. The work is based on two indicators of speed: the speed of rotation of the wheel and the speed of the car.
Special sensors always compare these two indicators as soon as the driver presses the brake pedal. If one or more wheels begin to lock up, that is, their rotation speed becomes less than the speed of the vehicle, the ABS is activated and artificially reduces the brake pressure on the wheel that caused the problem. As soon as the wheel speed is restored, the sensors give the command to again transfer the braking force to the hands (or rather, to the feet) of the driver.
The ABS system is activated/deactivated automatically up to 30 times per second. Therefore, during the operation of the anti-lock braking system, the driver feels a slight beating on the brake pedal. This factor suggests that the work is corrected by anti-lock braking.
In addition to the anti-lock braking system, high-end vehicles include a number of other technical innovations: traction control, emergency braking assistance, as well as a course stability system. All these technological gadgets originated from ABS and in fact are only assistants to the main anti-lock braking system.
Video: how ABS works.
Scope of application of anti-lock braking system
Today, ABS is used wherever there is a wheeled vehicle. Unless they have not yet decided to put it on warehouse loaders. The first area of use of the anti-lock braking system, as mentioned above, was aviation. When landing, the plane begins to move along the asphalt at great speed. The lack of ABS would require significantly longer stopping distances than at current airports, and safety would be less.
In addition to cars, ABS is also installed on motorcycles, ATVs and even trailers. Trucks would not be able to transport trailers with cargo on difficult winter roads if it were not for the help of the anti-lock system.
There is a lot of controversy and discussion around the use of ABS today. Experienced drivers sometimes argue that this is a useless technical innovation that overloads the braking system. But hundreds of thousands of drivers who have managed to avoid undesirable consequences in difficult traffic situations thanks to ABS will tell you the opposite.
- Burns, Robert - short biography
- The concept of common vocabulary and vocabulary of limited use
- Nancy Drew: The Captive Curse Walkthrough Nancy Drew Curse of Blackmoore Manor Walkthrough
- Deadpool - Troubleshooting
- Won't start How to Survive?
- What to do if bioshock infinite won't start
- Walkthrough Nancy Drew: Alibi in Ashes
- Spec Ops: The Line - game review, review Spec ops the line crashes on missions
- Room escape level 1 walkthrough
- Processing tomatoes with boric acid How much will 2 grams of boric acid
- Cucumber Grass (Borago)
- Bioinsecticide Lepidocid: purpose, properties and application procedure Lepidocide waiting period
- How to change the language to Russian in steam
- Dendrobium noble: room care
- Morphology of plants general concepts - document
- Planting, propagation and care of bamboo at home, photo Growing bamboo from seeds
- How to strengthen the cellular signal for the Internet in the country
- Sanskrit reveals the forgotten meaning of Russian words (2 photos)
- The oldest language Sanskrit programming language of the future Dead language Sanskrit
- Who has dominion over all the earth?









