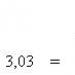Physics optical power of a lens. Lenses. Optical power of the lens
To characterize the optical properties of various lenses, the reciprocal of the focal length of the lens is often used. Value
is called the optical power of the lens.
The shorter the focal length, the stronger the lens refracts and the more. Thus, it can serve as a characteristic of the refractive power of the lens.
The unit of the optical power of a lens is taken to be the optical power of such a lens, the focal length of which is equal to; such a unit is called a diopter (dptr). The optical power of any lens (in diopters) is equal to one divided by the focal length (in meters). For converging (positive) lenses, the optical power is positive; for diverging (negative) lenses - negative. So, for example, a diverging lens with a focal length has an optical power.
These designations are well known to those who use glasses.
28. Using the method used to derive the lens formula, find the formula for refraction at a spherical interface between two media (for example, air - glass; Fig. 223).
29. Prove that focal lengths spherical surface (exercise 28) are related by the relation
where is the refractive index of the first medium, is the second medium.
30. Find the focal length of a plano-convex lens for which the radius of curvature of a spherical surface is . The refractive index of glass is 1.6.
31. A converging lens has a focal length The object is at a distance from the lens. Find the location of the image, as well as linear and angular magnification. Solve the problem numerically and graphically by drawing (to scale) an image of a small object in a lens.
32. Solve the previous problem for the case when the object is at a distance from the lens.
33. A concave mirror has radius . The object is located at a distance from the mirrors. Find the position of the image and the magnification of the mirror. Build an image and determine whether it is direct or reverse.
34. Indicate the position of the image in a thin lens if the source is on the main optical axis: a) at infinity; b) at double focal length; c) in the main focus; d) between the main focus and the lens.
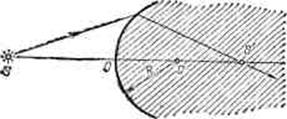
Rice. 223. To exercise 28
35. Analyze how the position and size of the image change when the position of the object changes for the following cases: a) a converging lens; b) diverging lens; c) concave mirror; d) a convex mirror.
36. The optical power of the lens is . Find its focal length.
37. Construct an image in the lens of a small segment inclined to the axis at an angle .
38. A flat mirror is rotated through an angle about an axis lying in the plane of the mirror and perpendicular to the incident beam; through what angle will the reflected beam turn?
In order to control light beams, that is, to change the direction of the rays, special devices are used, for example, a magnifying glass, a microscope. The main part of these devices is the lens.
Lenses are transparent bodies bounded on both sides by spherical surfaces.
There are two types of lenses - convex and concave.
A lens whose edges are much thinner than the middle is convex(Fig. 151, a).
Rice. 151. Types of lenses:
a - convex; b - concave
A lens whose edges are thicker than the middle is concave(Fig. 151, b).
The straight line AB passing through the centers C 1 and C 2 (Fig. 152) of the spherical surfaces that bound the lens is called optical axis.
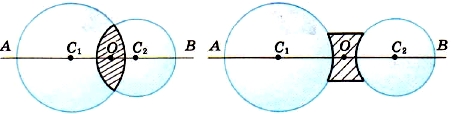
Rice. 152. Optical axis of the lens
By directing a beam of rays parallel to the optical axis of the lens to a convex lens, we will see that after refraction in the lens, these rays intersect the optical axis at one point (Fig. 153). This point is called lens focus. Each lens has two foci, one on each side of the lens.
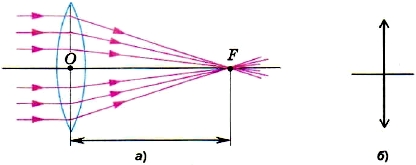
Rice. 153. Converging lens:
a - the passage of rays through the focus; b - its image on the diagrams
The distance from a lens to its focus is called lens focal length and is marked with the letter F.
If a beam of parallel rays is directed to a convex lens, then after refraction in the lens they will gather at one point - F (see Fig. 153). Therefore, a convex lens collects the rays coming from the source. Therefore, a convex lens is called gathering.
When rays pass through a concave lens, a different picture is observed.
Let's let a beam of rays parallel to the optical axis onto a concave lens. We will notice that the rays from the lens will come out in a divergent beam (Fig. 154). If such a divergent beam of rays enters the eye, then it will seem to the observer that the rays come out of point F. This point is located on the optical axis on the same side from which light falls on the lens, and is called imaginary focus concave lens. Such a lens is called scattering.
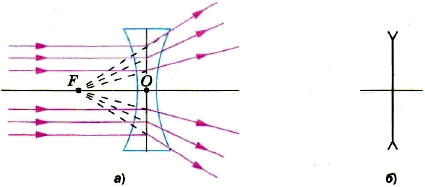
Rice. 154. Diverging lens:
a - the passage of rays through the focus; b - its image on the diagrams
Lenses with more convex surfaces refract rays more than lenses with less curvature (Fig. 155).

Rice. 155. Refraction of rays by lenses of different curvature
If one of the two lenses has a shorter focal length, then it gives a greater increase (Fig. 156). The optical power of such a lens is greater.

Rice. 156. Lens magnification
Lenses are characterized by a value called the optical power of the lens. Optical power is denoted by the letter D.
The optical power of a lens is the reciprocal of its focal length..
The optical power of the lens is calculated by the formula
The unit of optical power is the diopter (dptr).
1 diopter is the optical power of a lens with a focal length of 1 m.

If the focal length of the lens is less than 1 m, then the optical power will be greater than 1 diopter. In the case when the focal length of the lens is greater than 1 m, its optical power is less than 1 diopter. For example,
if F = 0.2 m, then D = 1 / 0.2 m = 5 diopters,
if F = 2 m, then D = 1/2 m = 0.5 diopters.
Since a diverging lens has an imaginary focus, we agreed to consider its focal length as a negative value. Then the optical power of the diverging lens will be negative.
The optical power of the converging lens was agreed to be considered a positive value.
- What is it in appearance lenses, you can find out which one has a shorter focal length?
- Which of the two lenses with different focal lengths gives the greater magnification?
- What is the optical power of a lens called?
- What is the unit of optical power called?
- The optical power of which lens is taken as a unit?
- How do lenses differ from each other, the optical power of one of which is +2.5 diopters, and the other -2.5 diopters?
Exercise 48
- Compare the optical powers of the lenses shown in Figure 155.
- The optical power of the lens is -1.6 diopters. What is the focal length of this lens? Is it possible to get a real image with it?
the optical power of the lens is 5 diopters, which means that the lens: Physics 8. Peryshkin
OPTICAL POWER
OPTICAL POWER
(Ф), characterizes the refractive power of axisymmetric lenses and systems of such lenses. O. S. - the reciprocal of the focal length of the system: Ф \u003d n "/f" \u003d -n / f, where n "and n are the media located respectively behind and in front of the system; f" and f - rear and front focal distances of the system measured from its main planes (see). For a system in the air (n=n""1), Ф=1/f". O. s. measured in diopters (m-1), it is positive for collecting systems and negative for scattering systems. Especially broadly the concept of "O. With." used in spectacle optics (see LENS, GLASSES).
Physical encyclopedic Dictionary. - M.: Soviet Encyclopedia. . 1983 .
OPTICAL POWER
(F) - value, F. is determined by f-le, where and are the angles of the paraxial beam with the axis of the system before and after refraction; h- beam intersection height with ch. planes H and H"; P" and . - refractive indices of media located respectively behind and in front of the optical. O. s. spherical surface radius r, separating two environments with P and P", is equal to Ф = ( p" - p) / r. O. F = n"/f " = n/f ;f"and f- rear and front focal lengths of the system (see. Cardinal points of the optical system). For a system in air ( n=n"= 1), Ф = 1/ f"O. s. is measured in diopters (m -1), it is positive for collecting systems and negative for scattering ones.
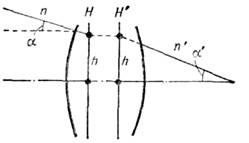
O. s. systems of two components (two lenses or two spherical surfaces) with O. s. F 1 and F 2 is determined by f-loy F \u003d F 1 + F 2 - dФ 1 Ф 2, where d- distance between back ch. the plane of the first component and the anterior ch. plane of the second for the case of two lenses in the air. for two spherical. surfaces (- the distance between the vertices of spherical surfaces, P" - refractive index of the medium).
The concept of O. with. especially widely used in spectacle optics (see also Lens).
Physical encyclopedia. In 5 volumes. - M.: Soviet Encyclopedia. Chief Editor A. M. Prokhorov. 1988 .
See what "OPTICAL POWER" is in other dictionaries:
Modern Encyclopedia
The value characterizing the refractive power of the lens (lens system); measured in diopters; optical power is the reciprocal of the focal length in m ... Big Encyclopedic Dictionary
optical power- OPTICAL POWER, a value characterizing the refractive power of lenses; measured in diopters and reciprocal of focal length in meters. For converging lenses, the optical power is positive, for diverging lenses it is negative. The concept of optical power ... ... Illustrated Encyclopedic Dictionary
optical power- The ratio of the refractive index of the image space to the back focal length. [Collection of recommended terms. Issue 79. Physical optics. USSR Academy of Sciences. Committee of Scientific and Technical Terminology. 1970] Subjects physical ... ... Technical Translator's Handbook
OPTICAL POWER- the value characterizing the refractive effect of O. s. lenses; related to the refractive index and focal length of the lens. O. s. is defined as the reciprocal of the focal length F of the lens (in meters): D = p) is expressed in (see). O. s. ... ... Great Polytechnic Encyclopedia
Optical power is a quantity characterizing the refractive power of axisymmetric lenses and centered optical systems from these lenses. The optical power is measured in diopters (in SI): 1 diopter \u003d 1 m 1. Inversely proportional to the focal ... ... Wikipedia
The value characterizing the refractive power of the lens (lens system); measured in diopters; optical power is the reciprocal of the focal length in meters. * * * OPTICAL POWER OPTICAL POWER, a value characterizing the refractive power ... ... encyclopedic Dictionary
optical power- viršūninė laužiamoji geba statusas T sritis Standartizacija ir metrologija apibrėžtis Dydis, atvirkščiai proporcingas lęšio užpakalinio židinio nuotoliui, kai objekto nuotolis yra begalinis. atitikmenys: engl. vertex power vok. Scheitelbrechwert … Penkiakalbis aiskinamasis metrologijos terminų žodynas
Characterizes the refractive power of axisymmetric lenses and systems of such lenses. O. s. there is a value inverse to the focal length of the system: φ \u003d n ’/f’ = –n / f, where n ’ and n are the refractive indices (See Refractive index) of the media, ... ... Great Soviet Encyclopedia
The value characterizing the refractive power of axisymmetric lenses and centered optical systems of such lenses; numerically equal to the ratio of the refractive index of the medium n in the image space to the rear focal length f: Ф = n / f ... Big encyclopedic polytechnic dictionary
Books
- Intraocular correction of aphakia. Monograph, Ioshin Igor Eduardovich. The intraocular lens is one of the most common implants in medicine, with hundreds of modifications. The optical properties of the intraocular lens are constantly being improved, and moreover…
Lenses are transparent bodies bounded on both sides by spherical surfaces.
Lenses are of two types: convex and concave.
A convex lens has much thinner edges than the middle.
A concave lens has thicker edges than the middle.
The straight line passing through the centers of the spherical surfaces bounding the lens is called optical axis.
By directing a beam of rays parallel to the optical axis of the lens onto a convex lens, we will see that after refraction in the lens, these rays intersect the optical axis at one point. This point is called lens focus. Each lens has two foci, one on each side of the lens.
The distance from a lens to its focus is called lens focal length. Denoted by letter F.
A convex lens is called gathering. Parallel rays directed at it, after refraction, are collected at one point F.
A concave lens is called scattering. Parallel rays directed at it exit the lens in a divergent beam. If this divergent beam of rays enters the eye, then it seems to the observer that the rays come out from the point F. This point is located on the optical axis on the same side from which light falls on the lens and is called imaginary focus concave lens.
Lenses with more convex surfaces refract rays more than lenses with less curvature.
The optical power of a lens is the reciprocal of its focal length.
The shorter the focal length of the lens, the more magnification it gives. That is, of the two lenses, the optical power is higher for the one with the shorter focal length.
The optical power of the lens is calculated by the formula:
1
D
= -
F
The unit of optical power is the diopter (dptr).
1 diopter is the optical power of a lens with a focal length of 1 m.
If the focal length of the lens is less than 1 m, then the optical power will be greater than 1 diopter. And vice versa.
It was agreed to consider the optical power of a diverging lens as a negative value, and for a converging lens as a positive value.
In order to control light beams, that is, to change the direction of the rays, special devices are used, for example, a magnifying glass, a microscope. The main part of these devices is the lens.
Lenses are transparent bodies bounded on both sides by spherical surfaces.
There are two types of lenses - convex and concave.
A lens whose edges are much thinner than the middle is convex(Fig. a).
Rice. Types of lenses:
a - convex; b - concave
A lens whose edges are thicker than the middle is concave(Fig. b).
The straight line AB passing through the centers C1 and C2 (Fig.) of the spherical surfaces that bound the lens is called optical axis.

Rice. Optical axis of the lens
By directing a beam of rays parallel to the optical axis of the lens onto a convex lens, we will see that after refraction in the lens, these rays intersect the optical axis at one point (Fig.). This point is called lens focus. Each lens has two foci, one on each side of the lens.

Rice. Converging Lens:
a - the passage of rays through the focus; b - its image on the diagrams
The distance from a lens to its focus is called lens focal length and is marked with the letter F.
If a beam of parallel rays is directed at a convex lens, then after refraction in the lens they will gather at one point - F (see Fig.). Therefore, a convex lens collects the rays coming from the source. Therefore, a convex lens is called gathering.
When rays pass through a concave lens, a different picture is observed.
Let's let a beam of rays parallel to the optical axis onto a concave lens. We will notice that the rays from the lens will come out in a divergent beam (Fig.). If such a divergent beam of rays enters the eye, then it will seem to the observer that the rays come out of point F. This point is located on the optical axis on the same side from which light falls on the lens, and is called imaginary focus concave lens. Such a lens is called scattering.

Rice. Divergent lens:
a - the passage of rays through the focus; b - its image on the diagrams
Lenses with more convex surfaces refract rays more than lenses with less curvature (Fig.).

Rice. Refraction of rays by lenses of different curvatures
If one of the two lenses has a shorter focal length, then it gives a greater magnification (Fig.). The optical power of such a lens is greater.

Rice. Lens magnification
Lenses are characterized by a value called the optical power of the lens. Optical power is denoted by the letter D.
The optical power of a lens is the reciprocal of its focal length..
The optical power of the lens is calculated by the formula
The unit of optical power is the diopter (dptr).
1 diopter is the optical power of a lens with a focal length of 1 m.

If the focal length of the lens is less than 1 m, then the optical power will be greater than 1 diopter. In the case when the focal length of the lens is greater than 1 m, its optical power is less than 1 diopter. For example,
if F = 0.2 m, then D = 1 / 0.2 m = 5 diopters,
if F = 2 m, then D = 1/2 m = 0.5 diopters.
Since a diverging lens has an imaginary focus, we agreed to consider its focal length as a negative value. Then the optical power of the diverging lens will be negative.
The optical power of the converging lens was agreed to be considered a positive value.
Homework.
Task 1. Answer the questions.
- How can you tell by the appearance of the lenses which one has the shorter focal length?
- Which of the two lenses with different focal lengths gives the greater magnification?
- What is the optical power of a lens called?
- What is the unit of optical power called?
- The optical power of which lens is taken as a unit?
- How do lenses differ from each other, the optical power of one of which is +2.5 diopters, and the other -2.5 diopters?
Task 2. Guess the rebus.

- Deadpool - Troubleshooting
- Won't start How to Survive?
- What to do if bioshock infinite won't start
- Walkthrough Nancy Drew: Alibi in Ashes
- Spec Ops: The Line - game review, review Spec ops the line crashes on missions
- Room escape level 1 walkthrough
- Processing tomatoes with boric acid How much will 2 grams of boric acid
- Cucumber Grass (Borago)
- Bioinsecticide Lepidocid: purpose, properties and application procedure Lepidocide waiting period
- How to change the language to Russian in steam
- Dendrobium noble: room care
- Morphology of plants general concepts - document
- Planting, propagation and care of bamboo at home, photo Growing bamboo from seeds
- How to strengthen the cellular signal for the Internet in the country
- Sanskrit reveals the forgotten meaning of Russian words (2 photos)
- The oldest language Sanskrit programming language of the future Dead language Sanskrit
- Who has dominion over all the earth?
- Symbols and amulets of Masons The famous Masonic amulet for money
- Hekate's father. Dark goddesses. Origin and genealogy
- nord wind airline fleet