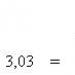What is profit, types. Types and their differences
Profit and income are the main indicators of the financial results of the production and economic activities of the enterprise.
Income is the proceeds from the sale of products (works, services) minus material costs. It represents the monetary form of the net output of the enterprise, i.e. includes wages and profits.
Income characterizes the total amount of funds that an enterprise receives for a certain period and, after taxes, can be used for consumption and investment. Income is sometimes subject to taxation. In this case, after tax is deducted, it is subdivided into consumption, investment and insurance funds. The consumption fund is used to pay staff and other payments.
Material costs include costs included in the corresponding element of the cost estimate for production, as well as costs equated to them for: depreciation of fixed assets, deductions for social needs, as well as other costs (except for labor costs).
Profit is the part of the proceeds that remains after the reimbursement of all costs for the production and marketing of products.
The amount of profit (income) is significantly affected by both the volume of products and its range, quality, cost, improvement of pricing and other factors. In turn, profit affects such indicators as profitability, solvency of the enterprise and others.
The total profit of the enterprise (gross profit) consists of three parts:
1) profit from the sale of products - as the difference between the proceeds from the sale of products (excluding VAT and excise duty) and its full cost;
2) profits from the sale of material assets and other property (this is the difference between the price of their sale and the costs of their acquisition and sale);
3) profits from non-sales operations, i.e. operations not directly related to the main activity (income from securities, from equity participation in joint ventures; renting out property; excess of the amount of fines received over those paid, etc.).
Allocate taxable income, i.e. profit calculated taking into account the provisions of tax legislation. This profit is the basis of income taxation. It differs from accounting profit, which is calculated from accounting data.
Net profit is the difference between gross profit and income tax. It remains at the disposal of the enterprise and is directed to consumption and accumulation funds. From the consumption fund, net profit is spent on the following purposes: payment of vouchers to employees, bonuses, gifts, etc. From the accumulation fund, the enterprise finances investment expenses: the acquisition of new fixed assets, construction, reconstruction, modernization, the acquisition of shares in other enterprises, etc.
Profit- excess of income from the sale of goods (services) over the costs incurred. In general, profit ( PF - profit) is defined as the difference between gross revenue and gross costs: PF = TR - TC. Profit is one of the generalizing estimated indicators of the activities of enterprises (organizations, institutions).
According to the nature of the costs incurred by the enterprise, there are:
1) accounting profit- the difference between gross income and explicit (accounting) costs;
2) economic profit- the difference between gross income and all costs (explicit and implicit);
In this regard, accounting profit (real money) is always greater than economic profit, which demonstrates the economic meaning of economic activity.
According to the size (value) of profit, there are:
1) negative profit (or loss situation)- a situation where gross costs exceed gross income ( TR< TC );
2) normal (or zero) profit- a situation where economic profit is zero. The situation of zero profit does not mean the unprofitability of each individual production, but it shows the equally efficient production of different entrepreneurs ( TR=TC );
3) positive economic profit- a situation where gross income exceeds gross costs ( TR > TC );
4) maximum profit achieved in the interaction of internal and external factors of the firm. The main requirement for profit maximization is the profitability of each unit of output. The firm seeks to maximize the difference between total revenue and total costs. The production of each additional unit of output increases the volume by the amount of marginal cost, but at the same time increases the total income - by the amount of marginal revenue.
As long as marginal revenue is greater than marginal cost, overall profit rises, its marginal maximization has not yet been reached, and the firm can increase output. As soon as marginal cost is higher than marginal revenue, the growth of total profit slows down and the increase in output becomes unprofitable. Therefore, profit reaches a maximum at such output, at which MR=MC .
Normal profit (zero economic profit) appears when the total revenue is equal to the total costs - external and internal. The amount of this profit largely depends on the entrepreneurial abilities of the owner of the company, who makes the main management decisions and bears the risks for investing his own and other people's funds. This benefit is also considered an element of implicit costs.
If the total revenue exceeds the costs calculated in this way, the company receives a net economic profit. Net economic profit means that this enterprise uses resources more efficiently than in the case of their alternative use. Net (economic) profit is the difference between gross income (you-handle) and total costs equal to the sum of external and internal costs. Net profit shows how profitable this area of activity is compared to other options. If the net profit is greater than zero, then this area is the most profitable; it is necessary to stay in this sphere. If the net profit is less than zero, then this means that there are more profitable options and you need to leave this area.
Accounting profit - the difference between gross income (revenue) and its external costs. If accounting profit is greater than zero, and net profit is less than zero, this means that the company incurs net losses (in another area, the return would be higher).
The calculation of economic profit is important for making managerial decisions and is carried out by economists, the calculation of accounting profit is used for tax purposes and is carried out by accountants. In order to achieve maximum profit, the firm must produce such a volume of output at which marginal revenue equals marginal cost: MR \u003d MC, where MR is the income that additional units of production bring).
The enterprise will receive the maximum profit when production costs of an additional unit will be equal to the additional income received from its realization. Profit maximization (loss minimization) is achieved at the volume of production corresponding to the equilibrium point of marginal revenue and marginal cost. This pattern is called the profit maximization rule. The profit maximization rule means that the marginal products of all factors of production are equal in value to their prices, or that each resource is used until its marginal product in monetary terms is equal to its value.
The main ways to increase profits: expanding production and capturing a larger market share; cost reduction associated with the introduction of new technologies in production and management; reduction of the tax burden; investments in the development of the company's human capital; search for new marketing strategies, etc.
Enterprise costs.
Production costs - the costs of firms associated with the consumption of resources or factors of production (buildings, equipment, raw materials and materials, hired labor) for the purpose of production and profit.
There are several approaches to the definition and classification of costs. The most well-known accounting and economic approaches. According to the accounting approach, costs are the value of the resources spent on production in the actual prices of their acquisition or procurement. According to the economic approach, this is the value of other benefits that could be obtained with the most beneficial of all possible alternative directions for using these resources. In the first case, we are talking about external (explicit) production costs, in the second - about internal alternative costs, also called implicit ones.
External costs (explicit, accounting) - payment for resources that do not belong to the firm (are attracted from outside). This category includes wages in the form of wages, land in the form of rent, capital in the form of expenditure on fixed and circulating assets, payment for the entrepreneurial abilities of the organizers of production and marketing. The sum of all external costs acts as the cost of production. The size of external costs largely determines the price level (cost method of pricing).
Internal costs (implicit) - the opportunity costs of using resources that are the property of the company (lost profit). Implicit costs are internal in nature and are not related to cash payments from the firm's accounts, and therefore are not included in the financial statements. An example is the cost of placing cash in shares. Implicit costs are the difference between the amount of dividends and the maximum possible income from lending this money at interest.
Explicit and implicit costs form the economic costs of the firm.
Transaction costs - costs in the field of exchange associated with the transfer of property rights. There are the following types of transaction costs:
1) costs of information search;
2) the costs of negotiating and concluding;
3) measurement costs;
4) costs of specification and protection of property rights;
5) the costs of opportunistic behavior. Opportunistic is the behavior of an individual who avoids compliance with the terms of the contract in order to profit at the expense of partners.
The presence of transaction costs pushes society to find both technical and organizational means to reduce them.
Production costs are classified taking into account the short-term and long-term periods. The short run is a period of time that is too short for a firm to change its production capacity. In this period, all resources remain unchanged and constant. Long-term period - a period of time long enough for the firm to have time to change the amount of all resources used, including changing the size of the enterprise. In this period, all resources are variable. The short-term period is a period of fixed capacities, and the long-term period is a period of varying capacities.
There are general, average and marginal costs.
Total costs (TC) - the costs required for the production of a certain amount of products.
Average cost (AC) - cost per unit of output.
Marginal costs (MC) - the costs associated with the production of an additional unit of output. Fixed costs do not affect marginal cost.
In the short term, the most important is the division of costs into fixed and variable.
Fixed costs (FC) - do not depend on the volume of production, will always occur even if the company does not produce anything: rent payments, deductions for depreciation of buildings and equipment, insurance premiums, salaries of top management personnel, utility costs, enterprise security , reimbursement of a bank loan, etc. Fixed costs remain unchanged at all levels of production, including zero.
Variable costs (VC) - related to output volumes (the more we produce, the more VC): the cost of wages, raw materials, fuel, energy, transport services, etc.
General (cumulative, gross) costs (TC) - the sum of fixed and variable costs of the company: TC = FС + VС, where FС - fixed costs; VC - variable costs.
In the long run, all costs are variable, their dynamics is determined by the nature of the economies of scale. The effect of a change in the scale of production may be positive or negative, in addition, such a change may not affect the productivity of the factors used. A positive effect occurs when, as the size of the firm grows, average production costs decrease due to: a higher level of specialization of the labor of workers and management personnel; the possibility of using more productive equipment; more complete waste disposal through the production of by-products.
All this contributes to economies of scale. A negative effect occurs when, as the size of the firm grows, average costs increase due to the complexity of managing large-scale production and instead of savings, there are losses or losses. The difference between the output at which the positive effect ends and the output at which the negative effect kicks in can be quite significant. Therefore, there is a period during which the average long-run costs will remain unchanged.
Least Cost Rule- the condition according to which costs are minimized when the last ruble spent on each resource gives the same return, the same marginal product. This rule ensures the equilibrium position of the producer.
An integral part of economic costs is " normal profit"- income from the use of entrepreneurial talent. Normal profit appears when the total income of the firm is equal to the total economic costs. In these conditions the firm's economic profit is zero. A normal profit is necessary to keep the entrepreneur in this field of activity.
Net economic profit
If a firm uses its available resources in the most efficient way and total income exceeds total, then there is a positive economic profit. Depending on the market structure and the ratio of elements of monopoly and competition in a particular market, economic profit can be maintained for a more or less long period.
The presence of positive or negative economic profit in the industry stimulates the inflow of new enterprises into the industry or the corresponding outflow of firms into other areas of activity.
Profit calculation example:3. Accounting profit (1 - 2) = 1000 - 800 = 200
4. Economic profit (1 - 2 - 3) = 1000 - 800 - 250 = -50
Conclusion: with positive accounting profit, economic profit turned out to be negative, i.e. the entrepreneur needs to analyze the possibility of alternative use of his funds.
Analysis of operating profit
Profits and losses are the financial results of the business activities of the enterprise.
The main objectives of profit analysis are:- verification of the validity of the planned profit. The plan for profit should be linked to the volume of products sold and its cost;
- assessment of the implementation of the business plan for profit;
- calculation of the influence of individual factors on the deviation of the actual amount of profit from the planned one;
- identification of reserves for further growth of profits and ways to mobilize (use) these reserves.
The most important sources of information for profit analysis are:
- (F. No. 1 reporting),
- (F. No. 2 reporting),
- accounting register - journal-order No. 15 for accounting for profit and its use,
- organizations.
- profit (or loss) from the sale of products, works and services;
- profit (or loss) from other sales;
- operating, non-operating and extraordinary income and expenses. The main part of the profit is profit from the sale of products, works, services.
- gross profit. It is defined as the difference between sales revenue and cost of goods sold;
- revenue from sales. It is calculated as the difference between revenue, cost, selling and administrative expenses;
- profit before tax is calculated taking into account the presence of operating and non-operating income and expenses;
- net income is determined by subtracting deferred tax assets and current income tax from profit before tax and deferred tax liabilities.
Let us analyze the profit received from the main activity of the enterprise, i.e. profit from the sale of products (works, services).
Profit from product sales- this is the financial result obtained from the main activity of the enterprise, which can be carried out in any form, fixed in its charter and not prohibited by law. The financial result is determined separately for each type of activity of the enterprise related to the sale of products, the performance of work, the provision of services. It is equal to the difference between the proceeds from the sale of products at current prices and the costs of its production and sale.
Pr \u003d Bp - C / s,
- Bp - sales proceeds;
- С/с - (production and sales costs).
Revenue is taken into account without value added tax and excises, which, being indirect taxes, go to the budget. The amount of markups (discounts) received by trade and supply and marketing enterprises involved in the sale of products is also excluded from the proceeds.
Enterprises engaged in export activities, when accruing profits, also exclude export tariffs directed to state revenue.
Revenue from sales of products is determined either as:
- its payment (for non-cash payments - to bank accounts; for cash - at the cash desk of the enterprise);
- upon shipment and presentation by the buyer of settlement documents.
In physical terms, the calculation of profit from the sale of products includes the balance of finished products at the beginning of the reporting period (He.), Unsold in the previous period, and the release of marketable products of the reporting period (TP) minus that part of the products that cannot be sold at the end of the reporting period (OK.).
Etc. = He. + TP - Ok.
A period is a quarter or a year.
The composition of the balances of unsold products at the beginning and end of the period depends: on the method of accounting for revenue chosen by the enterprise - on receipt of money to the settlement account (cash) of the enterprise or on the shipment of products, settlement documents for which are presented to the buyer.
Table No. 8 (in thousand rubles)|
Indicators |
According to the plan for actually sold products |
Actually |
|
|
1.Production cost of goods sold |
|||
|
2. Selling expenses related to products sold (sales expenses) |
|||
|
3. Total cost of goods sold |
|||
|
4. Proceeds from sales in sales prices, excluding VAT and excises) |
|||
|
5. Financial result - profit (p. 4 - p. 3) |
So, the profit from the sale of marketable products increased compared to the plan by the amount: 3376 - 3174 = + 202 thousand rubles. The following factors influenced this overfulfillment:
1. increase against the plan for the volume of sales. In the analyzed enterprise, the plan for the volume of sales (sales) of products was fulfilled by 101.6%. Multiplying the planned profit from sales by the percentage of overfulfillment of the plan in terms of sales volume, we find how much profit was received due to the growth in sales volume: (3174 * 1.6%) / 100% = + 50.8 thousand rubles. Consequently, due to the increase in the volume of sold products, the profit received from the sale increased by 50.8 thousand rubles;
2. An increase against the plan in the production cost of goods sold reduced profits.
Let's compare the actual and planned cost of actually sold products, i.e. let's compare the fourth column of the table with the third column on the first line: 19552 - 19491 \u003d - 61 thousand rubles. This result means that due to the increase in the production cost of goods sold, the profit decreased by 61 thousand rubles;
3. commercial (administrative) expenses, as well as production costs, have an inverse effect on profit. However, in this example, their value did not change and did not affect the profit. To establish this, let's compare the actual and planned values of commercial expenses attributable to the actual volume of sales of products, i.e. compare the fourth column of the table with the third column in the second line: 144 - 144 = 0
4. We establish the impact of changes in wholesale prices on profit from the sale of products by comparing the actually sold products in the current wholesale prices (excluding VAT and excises) and the actually sold products in planned prices (excluding VAT and excises).
To this end, let's compare the fourth column of the table with the third column on the fourth line: 23072 - 23087 \u003d - 15 thousand rubles. This result means that the wholesale prices for products sold decreased by 15 thousand rubles, which reduced profit by the same amount;
5. the impact of changes in the structure of sold products on profit is calculated by the balance method, i.e. as the difference between the sum of the deviation of the actual profit from sales from the plan and the sum of the influence of all other (already known) factors: 202 - (50.8 - 61 + 0 - 15) = + 227.2 thousand rubles. This result means that a shift in the structure (change in the structure) of sold products towards an increase in the share of more profitable types of products increased the profit from sales by 227.2 thousand rubles.
The total influence of all factors (balance of factors) is: + 50.8 - 61 +0 - 15 - + 227.2 = + 202 thousand rubles.
In this way, the above-planned profit from product sales was obtained mainly due to a shift in the structure of products sold towards an increase in the share of more profitable types of products, as well as due to an increase in the volume of product sales. At the same time, an increase in the cost of goods sold and a decrease in wholesale prices for products reduced profits. The amount of selling expenses did not change and did not affect the profit.
It is also important to analyze the "quality" of profits. Profit quality is a generalized characteristic of the structure of sources of profit formation. With a high "quality" of profit the volume of products produced increases, its cost decreases. With a low "quality" of profit there is an increase in sales prices for products in combination with the absence of an increase in the volume of production in physical terms.
The main thing in improving the "quality" of profit is to reduce. This is an intensive direction of increasing profits by mobilizing available reserves.
Marginal income
When analyzing profit from the sale of marketable products, it is necessary to determine such an indicator as marginal income. Marginal income is the difference between the proceeds from the sale of products and the variable costs of its production and sale. In other words, marginal income is the sum of fixed costs and profits from sales.
Based on this, the profit from the sale of marketable products is equal to marginal income minus fixed costs. It follows that the company will make a profit only if the fixed costs are reimbursed by the proceeds from the sale of a certain volume of manufactured products. This revenue should be sufficient to offset variable costs and generate profits. The analysis here allows you to establish, due to which particular costs (fixed or variable) included in the cost of goods sold, the profit changes.
Operating leverage effect
It is also necessary to consider such an indicator as operating leverage effect (production leverage). It is characterized by the ratio of marginal income and profit. The effect of operating leverage shows how much profit increases due to a change in revenue from product sales. The fact is that the effect of increasing sales revenue on the amount of profit depends on the ratio of variable and fixed costs. Therefore, the value of the operating leverage depends on this ratio. The higher the proportion of fixed costs, the greater the difference between marginal income and profit, and the higher the ratio between them. With the help of operating leverage, you can assess the degree of influence of revenue from the sale of products on profit. The greater the operating leverage, the greater the increase in profits provides each percentage increase in revenue from product sales.
An important aspect of profit analysis is definition of break-even(critical) volume of production and sales of products. There is a breakeven output if equals(or if marginal income is equal to the sum of variable costs as part of the cost of production). In this case, the organization does not receive any profit or loss from the sale of products. This situation is called the critical (break-even) volume of production and sales, or otherwise, the critical point (break-even point), as well as threshold.
The critical volume of production can be defined as the quotient of the amount of marginal income. Therefore, the threshold of profitability can be determined by the following formula:
(sum of variable costs/sum of marginal income) * 100%.
To reach the critical point, it is necessary to produce and sell so many products that both the variables and the given organization are covered by the proceeds from the sale. In order to make a profit, you should increase sales. If the value of production decreases, then the organization will receive a loss.
All the factors listed in this paragraph that affect the amount of profit received should be attributed to the number internal factors. In addition to them, there are external factors, which also determine the amount of profit received by the organization.
External factors include:- socio-economic conditions in which the organization operates;
- degree of development of foreign economic relations;
- transport conditions;
- the level of prices for production resources, etc.
Analysis of profit from the sale of assets, operating, non-operating and extraordinary income and expenses
Reserves for increasing profits and increasing the level of profitability
Enterprises can receive financial results (profits or losses) that are not related to the sale of products, works and services. This includes, in particular, gains and losses from so-called other sales, i.e. from the sale of property (assets) of the enterprise. For example, there may be a sale (of funds), materials, and other types of enterprise assets.
When analyzing financial results from other sales, it is necessary to check the reliability of the valuation of the assets being sold, as well as to compare the possible income from the sale of assets with the estimated costs of these operations. Then, already in the process of subsequent analysis, the actual financial result from other sales should be compared with the envisaged result.
When selling fixed assets, one should compare the possible profit from their sale with the income that can be received by the enterprise if these fixed assets continue to operate. If the profit from the sale of an object of fixed assets exceeds the amount of possible profit from the continuation of the operation of this object for a certain standard period, then the sale of this object of fixed assets should be carried out.
In addition to profits and losses from other sales (from the sale of assets), organizations may also have non-operating financial results that are not related either to the sale of products or to the sale of assets (property).
Non-operating financial results are divided into three types:
- operating income and expenses;
- non-operating income and expenses;
- emergency income and expenses.
- interest receivable;
- Percentage to be paid;
- income from participation in other organizations;
- other operating income and expenses.
- insurance indemnities;
- the cost of material assets remaining from the write-off of assets unsuitable for restoration and further use, i.e. fixed assets.
Extraordinary expenses arise as a consequence of extraordinary circumstances of the economic activity of the enterprise (floods, fires, accidents, or nationalization of property, etc.)
Operating, non-operating and extraordinary financial results are generally not planned. Therefore, the main method of their analysis is to compare their actual value for the reporting period with the amounts for previous reporting periods, i.e. study of the dynamics of these quantities. When analyzing for each type (item) of these incomes (profits) and expenses (losses), it is necessary to find out the reasons for their occurrence, to establish whether measures were taken to pay off the debt in a timely manner, to identify the persons guilty of missing the statute of limitations, etc.
Analysis of non-operating financial results makes it possible to assess the organization of the functioning of marketing and financial services, as well as the degree of compliance with contractual discipline.
In conclusion of the analysis, it is necessary to develop specific measures aimed at reducing or even completely preventing losses from non-sales operations.
The analysis of profit formation should be completed with a summary calculation of the reserves for increasing profits identified as a result of the analysis.
The main reserve for profit growth is the reduction in the cost of manufactured and sold products.

Analysis of the use of profits
The amount of profit remaining at the disposal of the enterprise (net profit) is primarily affected by the amount of taxable profit, as well as the income tax rate.
If taxable income changes, then net income changes in the opposite direction. So, with an increase in the amount of taxable profit, the amount of profit remaining at the disposal of the enterprise will decrease.
With regard to income taxed at rates different from the income tax rate, these incomes are deducted from gross income when determining the amount of taxable income. The considered types of income, with the exception of taxes, increase the amount of profit remaining at the disposal of the enterprise.
The amount of deductions from profit in has the opposite effect on the amount of net profit: with an increase in these deductions, the profit remaining at the disposal of the enterprise decreases, and with a decrease in these deductions, net profit increases.
When analyzing the use of profit, it is necessary to compare its actual distribution for the reporting period with the distribution provided for in the financial plan of the enterprise, as well as with the corresponding data for previous periods, that is, in dynamics. Based on the analysis of the use of profit, conclusions can be drawn about the need for changes in its use in order to achieve optimal ratios between the individual areas of its distribution.
The constituent documents of each organization determine the procedure for using the net profit remaining after making tax payments to the budget, as well as the list of funds formed from this profit.
In the process of analyzing the use of profits, the following main tasks should be solved:- establish how the amounts and specific weights of specific areas for the use of profit have changed in comparison with the financial plan and the values of the previous period;
- to analyze the formation and use of reserve capital and other special funds;
- evaluate the efficiency of profit use;
- determine ways to optimize the use of profits and the main activities aimed at improving the use of profits.
In the process of formation and use of special purpose funds at the expense of the profit remaining at the disposal of the organization, the stimulating role of profit is carried out.
The following questions should be considered when reviewing special funds:- change in the amount of funds allocated to special funds;
- the influence of individual factors on this amount;
- the procedure for using special funds for the relevant purposes;
- how the amounts of deductions from net profit to special funds and the amounts of use of the funds of these funds change in dynamics, i.e. over time;
- what are the reserves for optimizing the size of special funds and their use.
When analyzing the formation of special-purpose funds at the expense of net profit, a formula should be used to determine the degree of change in deductions to special funds due to changes in net profit:
∆SF = ∆CHP K,
- ∆SF— increase in the value of special funds, i.е. accumulation or consumption fund by changing the amount of profit remaining at the disposal of the enterprise;
- ∆CHP- an increase in the amount of profit remaining at the disposal of the enterprise;
- To— coefficient of deductions from net profit to this fund (basic value).
The amounts of contributions to special purpose funds are also influenced by changes in the value of the coefficient of contributions from net profit. The influence of this factor can be determined by the following formula:
∆SF \u003d (K 1 - K 0) PE 1,
- ∆SF- increase in the value of special purpose funds due to changes in the coefficient of deductions from net profit;
- K 1 , K 0- respectively, the actual and basic coefficients of deductions from net profit to special-purpose funds;
- PE 1— net profit of the given enterprise for the reporting period.
An increase in the amount of profit remaining at the disposal of the enterprise accordingly increases the amount of deductions to special funds, and a decrease in net profit reduces the amount of these deductions. Similarly, i.e. the change in the coefficient of deductions from net profit also directly affects: with an increase in this coefficient, the amount of deductions to special-purpose funds increases, and with a decrease in the value of the coefficient, the amount of deductions to special funds decreases.
In the process of analyzing the use of special funds, it is necessary to compare the actual expenditures of funds with the planned and expenditures of previous reporting periods. Thus, the funds of accumulation funds are directed, as a rule, to the development of production, i.e. to increase (funds), as well as to fill current assets. It is advisable to analyze how the use of the accumulation fund has affected the structure of the property of the enterprise, as well as the technical condition of fixed assets (funds).
Consumption funds are spent to make various social payments. It is advisable to analyze the use of these funds in conjunction with such indicators of the state and use of labor resources, such as turnover rates for hiring and dismissal, full turnover, turnover, indicators of the average wage category, and labor productivity. The use of profit for the formation and spending of consumption funds is justified if it is interconnected with the improvement of the listed labor indicators.
Giving a general assessment of the use of the organization's profits, it is necessary to state how it contributes to the increase in the scale of the organization's activities, the growth of its economic potential, the replenishment of equity, as well as the optimization of the structure of the organization's assets and liabilities.
Any company is opened with the aim of making a profit and earning. However, this concept itself is rather vague, therefore it is worth considering it from different angles in order to separate each meaning from each other.
A good leader must be well versed in terms and be able to independently calculate the profitability of the enterprise. Initially, this work may seem complicated, but in reality it is not quite so.
What is profit?
Profit or, in other words, gross income is the main source of funds of any enterprise. It enters the company's assets in the form of cash and non-cash funds at the expense of:
- sales of goods;
- provision of services.
All material costs that are paid at the expense of these funds are not included in the concept of profit. Any company should strive to get the largest amount of it.
Gross income is an estimate. Even an enterprise that can only cover expenses at the expense of its own profit will be considered unprofitable. In this case, the very meaning of the existence of such an organization is lost.
This situation gives rise to only two solutions:
- carrying out cardinal reforms;
- closure of the enterprise.
In addition, do not forget that profits provide profitability to the state through direct taxation.
Income tax is common throughout the world and differs only in rates for various categories of taxpayers.
If we talk about income in general, then they perform certain functions:
- They act as a criterion for evaluating the activities of a particular company (the higher the profit, the better the company works in its segment).
- They act as an incentive for development (any entrepreneur seeks to increase profits, which means to work better and with greater returns).
- Determine the difference between spending and earning.
With high and stable profits, the enterprise, as a rule, develops: new equipment is purchased, new specialists are hired, areas are expanded, new technologies are being introduced. And this ensures the growth of the state economy.
Main types of profit
Let's talk about different types of profit. These concepts must be clearly separated.
Gross
The most important indicator of the development of the company is the gross profit. It is according to its value that the efficiency of work is calculated.
Gross profit is the difference between the amount received from the sale of goods and services and their cost.
It is calculated by the formula: VP \u003d Vyr-Seb, where:
- VP - gross profit;
- Seb - the cost of goods and services.
For example, consider data from the financial report of one of the enterprises. They are shown in the table below.
We calculate the gross profit: 220,000 - 75,000 \u003d 145,000 rubles.
Profit analysis is a very important issue. Any large company interested in its development in the market carefully studies all types of profits and considers their dynamics as the main indicator of stability.
margin
Another concept of profit lies behind the word "marginal". This income, in fact, is the difference between the profit from the sale of goods and services of the company (excluding value added tax) minus variable costs. The calculation formula is as follows:
MP=Vyr-PZ
- MP - marginal profit;
- Vyr - proceeds from the sale of goods and services;
- PV - variable costs.
Accounting in Russia does not allow allocating variable costs to a certain volume of production. That is why they take the technological cost for them.
An example of a calculation is as follows: if it is known that the cost was 40,000 rubles, and the revenue was 120,000, then the marginal profit = 120,000 - 40,000. Total 80,000 rubles.
 If everything is very clear with revenue, then the concept of variable costs should be explained. So, these include the following costs:
If everything is very clear with revenue, then the concept of variable costs should be explained. So, these include the following costs:
- payment of salaries to employees;
- funds spent on raw materials for production;
- payment for electricity, gas and water;
- other expenses.
With the expansion of production marginal profit increases, and variable costs decrease. Often this concept is called the contribution to the coverage, since it is the source for:
- formation of new profit;
- cover the fixed costs of running the company.
The amount of marginal profit directly affects the amount of net income of the company.
operating room
This type of profit is not typical for accounting and economic accounting at Russian enterprises, however, having come to us from Western analytics, this concept has become stronger today. Let's figure out what exactly is meant by this definition.
Increasingly, economists come across the concept of EBIT. It denotes operating income, and literally translates as profit before interest and taxes are paid. The indicator is determined by the following formula:
OP \u003d VP-KR-UR-ProchR + PVyp + ProchD
- OP - operating profit;
- VP - gross profit;
- CR - commercial expenses;
- SD - management costs;
- OtherR - other expenses;
- PVyp - interest payable;
- Other income - other income.
Consider an example of a calculation based on a table with line codes. Based on it, it is very convenient to calculate the results.
| Index | The code | 2015 |
|---|---|---|
| Gross profit | 2100 | 200 000 |
| Management costs | 2220 | 30 000 |
| Commercial costs | 2210 | 11 000 |
| Other expense | 2350 | 5 000 |
| Other income | 2340 | 3 000 |
| Interest payable | 2330 | 17 000 |
Let's perform a simple calculation using the formula: 200,000 - 11,000 - 30,000 - 5,000 + 17,000 + 3,000 = 174,000 rubles.
The definition of operating income is very difficult for us to understand, but if you understand it, you can calculate the effectiveness of any type of company activity.
Below we will consider the term book profit, which is directly related to operating profit. If the balance sheet income is known, then the formula for calculating the operating income will be simple:
OP \u003d BP + PVyp, where:
- OP - operating profit;
- BP is book profit;
- PVyp - interest payable.
The calculations here are directly related to the interest payable, and if they are not, then it is advisable to calculate the balance sheet income.
balance sheet
The indicator of book profit is extremely important when paying taxes. It is very similar to the operating room. This is the type of income that is received before taxes are paid.
Balance sheet income is an indicator of the company's performance and its financial results. The formula is:
BP=Vyr-Seb+ProchR+ProchD
- BP - balance sheet profit;
- Vyr - revenue;
- Seb - all costs for the cost;
- OtherR - other expenses;
- Other income - other income.
As an example, consider financial statements with line numbers in a table. And we will solve the problem using the existing formula.
We calculate: 200,000 - 60,000 + 5,000 + 1,000 = 146,000 rubles.
This indicator is reflected in the reporting. If calculated incorrectly, it can not only distort the results, but also cause fines.
Pure
 The definition of net income is very simple. It reflects income received after paying taxes and other expenses. Calculation formula:
The definition of net income is very simple. It reflects income received after paying taxes and other expenses. Calculation formula:
PE \u003d Vyr-Seb-UR-KR-ProchR-Tax, where:
- PE - net profit;
- Vyr - proceeds from the sale of goods and services;
- Seb - the cost of goods and services;
- CR - commercial expenses;
- SD - management costs;
- Other - other expenses.
You can take as a basis a different formula, based on the values of profit:
PE \u003d FinP + VP + OP-Tax, where:
- PE is net profit;
- Finp is financial profit;
- OP - operating profit;
- VP - gross profit.
Consider an example:
| Index | The code | 2015 |
|---|---|---|
| Revenue | 2110 | 200 000 |
| Cost price | 2120 | 60 000 |
| Commercial costs | 2210 | 11000 |
| Management costs | 2220 | 13000 |
| Other income | 2340 | 5 000 |
| Other expense | 2350 | 1 000 |
| Profit balance sheet | 2300 | 146 000 |
| income tax | 2410 | 15100 |
We calculate: 200,000 - 60,000 - 13,000 - 11,000 - 1000 - 15100 \u003d 99,900 rubles.
According to the concept, the amount of net profit is the balance on the account of the enterprise, which will be an indicator of its effective work. The higher this indicator, the more significant the growth. If over time this indicator falls, then this indicates a decrease in efficiency.
Net profit is analyzed by two popular methods:
- Statistical. According to this analysis, it is possible to make a forecast of changes in the rate of return.
- Factorial. In fact, it identifies the most important factors influencing the growth of net profit.
The ratio of types of profit
The direct relationship between different types of profit is obvious. Even on the basis of simple calculation formulas, one can notice that often one indicator correlates with another. This is no coincidence.
When conducting accounting, losses and profits are reflected in a document of a certain form “Report on financial results”. This information should always be at hand. The calculation of one type of income may depend on the estimate of another. So, for example, the income from the sale of goods is directly related to the gross profit indicator.
How to calculate profit from sales?
Return on sales is calculated based on profit. It is very important to understand what percentage of profit the company receives by spending certain amounts. For this, the formula is used:
Pp=VP-UR-KR, where:
- Пп - profit as a percentage;
- VP - gross profit;
- CR - commercial expenses;
- SD - management costs.
Below is a table on the example of the sale of one unit of goods for the billing period:
To determine the amount of net profit, you need to subtract tax deductions and other expenses from the amount of profit from sales.
Factors on which the amount of profit depends
 It is economically justified to divide all factors affecting profit into two main groups:
It is economically justified to divide all factors affecting profit into two main groups:
- external;
- internal.
They are considered separately, since they are little related to each other. Let's talk about external factors.
Among them are:
- the general situation on the market, the level of supply and demand (in other words, market conditions);
- the influence of state policy (the size of tax rates, regulation of tariffs, fines, provision of benefits, etc.);
- natural conditions;
- the price level in the market;
- depreciation rates.
As for internal factors, they are divided into production and non-production. The first are those that directly relate to the subjects of labor activity and financial resources. And the second - depend on the activities of the supply and marketing, as well as the parameters of working conditions.
Internal factors include:
- competitiveness of goods and services in the market;
- labor productivity;
- quality of management;
- planning efficiency;
- the level of organization of labor and management;
- rationality of spending resources.
Some factors affect the profit margin directly, while others indirectly.
Analysis of the results
Economic analysis in production is very important. Even if the company is just getting on its feet, it is necessary to carefully study the profits received and, if possible, make forecasts.
All this is the work of an accountant. An analysis of the activities of any company is accompanied by a tax report of each period. In this case, the enterprise should be considered as a separate object. Another thing is how well the market was initially analyzed based on:
- the cost of goods;
- its value in the market;
- the impact of competition, etc.
This directly affects the quality indicator, which is income. How the company will develop in the future depends on the competence of management and economists. Analysis allows you to find the right solutions for any development of the situation.
Any business operates in order to generate income. Knowledge on this topic is never superfluous. Today the market is developing rapidly, a huge number of factors can affect this. That is why it is so important to analyze and always keep your finger on the pulse.
Profit is the difference between revenue (income) and costs (expense). Profit is a key measure of the financial efficiency of entrepreneurial activity.
In the financial statements (Profit and Loss Statement), the following profit indicators are distinguished:
- (loss) - the difference between the sales proceeds without VAT and the cost of sales;
- profit (loss) from sales - gross profit minus commercial and administrative expenses;
- profit (loss) before tax (profit (loss) from sales plus interest and other income and expenses, except for income tax);
- net profit (loss) - the final financial result, taking into account all the income and expenses of the organization.
What does profit depend on?
If we consider profit as an accounting indicator, then profit is determined by the difference between the proceeds from the sale of products and the costs of its production. Making a profit is the main goal, by definition, of any commercial activity. In an economic sense, the profit that an entrepreneur receives is directly dependent on risk. The higher the entrepreneurial risk, the higher the profit.
Profits are influenced not only by financial factors (the cost of raw materials or production efficiency), but also by market factors. For example, an enterprise can make more profit if it has a monopoly in the market and can dictate its own (inflated) prices for products to customers.
Profit Analysis
A general profit analysis can be performed according to the financial statements - Profit and Loss Statement (for example, automatically, using). In particular, the change in profit is analyzed (analysis in dynamics), as well as profitability ratios. For profit analysis, two types of coefficients are used. In the first, profit is compared with another "turnover" indicator - revenue or cost (for example, return on sales). In the second - profit is calculated in relation to the value of assets or capital involved in its creation (for example, return on assets, return on equity).
For a deeper analysis of the factors that influenced the financial result, both accounting data (including cost data by items, elements) and external data (for example, a drop in demand, a worsening economic situation in the country) are used.
Profit taxation
Along with value added, which is subject to VAT, the main object of taxation for commercial organizations is profit. At the same time, it is a direct tax, it is paid by the enterprise from its own funds, while VAT is paid at the expense of the buyer.
The current income tax rate in the Russian Federation is 20% (with an increased tax rate for certain types of activities). There are also special tax regimes (for example, the simplified taxation system), where profits (revenues minus certain expenses) are taxed at a lower rate.
Still have questions about accounting and taxes? Ask them on the accounting forum.
Profit: details for an accountant
- Income tax in 2018: clarifications of the Ministry of Finance of Russia
... /1/70711 If a taxpayer distributing profits for each separate division for ... the taxpayer does not have the amount of income tax payable in the Russian Federation ... income is subject to corporate income tax in the generally established manner. The letter ... has the right to reduce the amount of corporate income tax (advance payment) subject to ... received by the taxpayer in the course of carrying out profit-making activities, with the exception of those named in ...
- income tax in 2017. Clarifications of the Ministry of Finance of Russia
The calculated amount of dividend income tax. When taxing the above income ... amounts of tax similar to corporate income tax paid by a Russian organization (... amounts of tax similar to corporate income tax paid by a Russian organization (withheld ... in accordance with the provisions of the article "Profit from entrepreneurial activity" corresponding ... in accordance with the provisions of the article "Business profits" of the relevant ...
- Income tax benefits for participants in innovative projects
Once this happens, the profits earned are subject to the general tax... by the corporate center, then the profits received by it are subject to the general rate of... period. This does not take into account the profit (loss) received (received) on the basis of ... for exemption from taxation. The received profit is subject to taxation at the rate of 0 ... for organizations paying income tax. As noted in the Letter of the Ministry of Finance ... the right to reduce the amount of income tax (advance payment) calculated by him on ...
- General and special income tax rates
Reduced income tax rates to be credited to the budgets of the subjects ... a reduced income tax rate (not higher than 13.5%) is established, ... reduced corporate income tax rates to be credited to the federal ... a reduced the rate of income tax to be credited to the budgets of these ... tax accounting was for the first time received profit from the sale of goods (works, ... RF at a rate of 0% is taxed on profits received by an organization with the status: ...
- The Ministry of Finance recalled what has changed in PBU 18/02 on income tax calculations
The definition of the current income tax has been clarified; 5. The definition of temporary ... used to reduce income tax in the reporting period, but ... and expenses that form accounting profit (loss) and tax base ... operations that are not included in accounting profit (loss), but forming tax ... information: on deferred income tax; on the values that explain the relationship ... indicators related to corporate income tax. Changes are applied by organizations starting...
- Submitting an amended income tax return
Taxable income tax base. The question arises: how to correct ... in cases with respect to income tax errors occur Correction of errors ... when calculating income tax (from the Resolution of the Presidium of the Supreme Arbitration Court ... amended income tax return. Overpayment of taxes, ... p. four). Income tax payable after the expiration of the tax ... and income tax return, the Federal Tax Service has the right to request additional ... submission of an income tax return for the corresponding reporting (tax) ...
- An example of filling out an income tax return when paying dividends
Income tax return sheets for organizations paying dividends. B... income tax return sheets for organizations paying dividends. Procedure ... sheet 03 "Calculation of income tax withheld by a tax agent (source ... of a tax agent - 1 (organization distributing profits). Type of dividends - 2 (according to ... used to calculate income tax, for Russian organizations (rate... used to calculate income tax for Russian organizations (rate...
- Legality of using tax clauses on the example of personal income tax, VAT and income tax
And in an effort to increase their profits, everyone invents in the process of work ... An organization becomes a tax agent for income tax upon payment of income ... the obligation to pay income tax arises with the buyer - a foreign ... organization, it remains to pay income tax just for yourself. According to article ..., impose the obligation for income tax on another business entity ... personal income tax, VAT or income tax (with the exception of organizations that apply special ...
- Advance income tax payments. Examples
For income tax. An organization paying income tax must pay ... advance payments and income tax administrative responsibility is provided in the form ... Sheet 02 Accounting Accounting profit (loss) is the final financial ... organization reflects the amount of income tax determined based on accounting profit... . Advance payments on income tax The organization pays quarterly We will give the necessary ...
- Separate subdivisions of UE and income tax
The vastness of the topic of calculating income tax by payers with OP, numerous ... the vastness of the topic of calculating income tax by payers with OP, numerous ... two options are possible: 1. Profit is distributed among all separate divisions .... 2. Profit is not determined for each ... Thus, income tax is mainly paid to the budgets of those ... period. Continuation of the example Taxable income for the whole enterprise for ...
- The procedure for filling out an income tax return for 9 months of 2016
Failure to submit an income tax return For violation of the deadline for submitting ... an income tax return To verify the correctness of filling out the declaration ... for income tax, you can use the developed by the Federal Tax Service ... and losses that reduce taxable income in 2016. Final value. .. filling out the income tax return, you can use the developed by the Federal Tax Service ... accruals and calculates income tax on a quarterly basis. Non-operating expenses of the company ...
- 0% income tax rate for medical and (or) educational activities: there is little time left to apply it
Zero rate on income tax According to paragraph 3 of Art. ... in the income tax return for this period, zero ... zero income tax rate for medical organizations is applied, ... 0% for income tax, see also letters from the Ministry of Finance ... submission of income tax returns (no later than March 28), ... that the amount of income tax will be recalculated at the general rate ... % when calculating income tax for 2015, since ... 0% income tax is due not only to compliance by the organization. ..
- Cash basis for income tax purposes
Organizations use the accrual method when calculating income tax. But ... organizations apply the accrual method when calculating income tax. But ... the purposes of calculating corporate income tax are determined in accordance with ... advance payments on income tax from the beginning of the year; file... an amended income tax return. Features of accounting for expenses when ... reducing the base for income tax, in the manner provided for in paragraphs. ... the income tax base, the specified subsidy is subject to reflection ...
- TOP-10 clarifications of the Ministry of Finance of Russia on income tax in 2018
The tax base for corporate income tax. Letter dated October 29... tax base for corporate income tax. Letter dated August 6 ... the tax base for corporate income tax only on the basis of an agreement ... to the budget of the amount of income tax within the period established by paragraph two ... the taxpayer does not have the amount of income tax payable in the Russian Federation .. subject to the payment of income tax in the Russian Federation. Letter from...
- Income and expenses on income tax in a state institution
From income taxation on income received by a state institution ... or from income taxation on income received by a state institution ... These incomes are subject to income tax in the generally established manner. Rationale. ... exempts income from income tax: in the form of funds, ... such income is subject to income tax in accordance with the generally established procedure. In ... from taxation on income on the basis of paragraphs. 33 ... is exempt from income tax on the basis of paragraphs. 33. ...
In this article, we will consider net profit, the calculation formula, the definition and its role in the financial analysis of the enterprise. Knowing the value of net profit allows business leaders to assess the effectiveness of activities for the reporting period. Net profit has a great influence on the future development of the enterprise, its competitiveness, investment attractiveness, solvency and financial reliability.
Net profit. Definition
Net profit(EnglishNetIncome,Netprofit,Netearnings) - is the most important indicator of financial analysis and represents the final rate of return, which remains after deducting all costs, including taxes.
The formula for calculating the net profit of an enterprise
To calculate the net profit, all costs and taxes of the enterprise must be deducted. The formula has a single economic meaning, but can be reflected in different ways:
Net profit = Revenue – Cost of goods – Administrative and selling expenses – Other expenses – Taxes;
Net profit= Financial Profit + Gross Profit + Operating Profit - Amount of Taxes;
Net profit= Profit before tax - Taxes;
Net Income= Total Revenue – Total Expenses.
Net profit is also called “the bottom line” (bottom line), because it is reflected in the balance sheet as the last line. In the balance sheet until 2011, net profit was reflected in line 190 of Form No. 2 (Profit and Loss Statement), after 2011, the net profit indicator is reflected in line 2400.
The formula for calculating net profit on the balance sheet
Let's write in more detail the formula for calculating net profit through the balance lines.
Net income (line 2400)= Revenue (line 2110) - Cost of sales (line 2120) - Selling expenses (line 2210) - Administrative expenses (line 2220) - Income from participation in other organizations (line 2310) - Interest receivable (line 2320) – Interest payable (line 2330) – Other income (line 2340) – Other expenses (line 2350) – Current income tax (line 2410)
The figure below shows a part of the balance sheet of the enterprise OJSC “Surgutneftekhim” and its reporting for 5 years. As you can see from the balance sheet in Excel, in order to get net profit, you must first calculate: gross profit (marginal profit), profit from sales and profit before tax.

The place of net profit in the enterprise income system
Net profit occupies a key position in the income system of the enterprise. In order to understand, consider its relationship with other types of income. The figure below shows the types of profit and their relationship. Each type of profit allows you to evaluate the effectiveness. So marginal profit shows the effectiveness of sales and sales of products. (You can learn more about this type of profit in the article: ““) Operating profit reflects the efficiency of production or another type of core activity of the enterprise Profit before tax is profit without taking into account other costs / income from non-core activities. As a result, net profit, cleared of all costs and expenses, shows the integral result of the functioning of the enterprise.

Purposes and directions of using the net profit indicator
The amount of net profit characterizes the efficiency of the entire company / enterprise and is used for various purposes by various external and internal stakeholders (persons, users).
| User/stakeholder | Purpose and directions of use |
| Investors | Purpose: assessment of investment attractiveness Assessment of the size and dynamics of changes in the net profit of the enterprise to analyze its investment attractiveness. The more an enterprise can generate net profit at the end of the reporting period, the higher its profitability. |
| Lenders | Purpose: creditworthiness assessment Assessment of the size and dynamics of changes in net profit to analyze the solvency and creditworthiness of the enterprise. Money is the fastest liquid asset, and the more cash a business has left after paying all tax deductions, the greater its ability to meet its obligations in the short and long term. |
| Owner/Shareholders | Purpose: assessment of the effectiveness of activities in general The analysis of net profit is an integral indicator of the activity of an enterprise/organization and characterizes the effectiveness of all management decisions for the reporting period. The larger the net profit, the more effective was the management of the organization. Growth in net income increases the size of dividend payments and allows attracting additional buyers/shareholders. |
| Suppliers | Purpose: assessment of the sustainability of functioning The net profit of an enterprise serves as an indicator of its sustainable development. The higher the net profit for the reporting period, the higher the ability to pay suppliers and contractors for raw materials on time. |
| Top managers | Purpose: assessing the sustainability of financial development The size of net profit and the dynamics of its change serve as a guideline for developing strategies and plans to increase it at the operational level. Planning of deductions to reserve funds, payroll funds and production funds. |
Methods for analyzing the net profit of an enterprise
Let's consider various methods of the analysis of net profit of the enterprise. The purpose of this analysis is to determine the factors, causal relationships between indicators that affect the formation of net profit as the final performance indicators of the enterprise.
We can distinguish the following methods of analysis, which are most often used in practice:
- Factor analysis;
- Statistical analysis.
These types of analysis are opposite in nature. So factor analysis focuses on determining the significant factors that affect the formation of the net profit of the enterprise. Statistical analysis focuses on the use of time series forecasting methods and is based on an analysis of the nature of changes in net profit by years (or other reporting periods).
Factor analysis of the net profit of the enterprise
The main factors in the formation of net profit are presented in the formula described earlier. To assess the influence of factors, it is necessary to evaluate their relative change for 2013-2014 and absolute. This will allow the following conclusions to be drawn:
- How did the factors change during the year?;
- What factor had the maximum change in net income?
In financial analysis, these approaches are called "Horizontal" and "Vertical analysis", respectively. The factors that form the amount of net profit and their relative and absolute changes during the year are shown below. The analysis was made for the enterprise OJSC "Surgutneftekhim".

As we can see, during 2013-2014, other expenses and other income changed to the maximum. The figure below shows the change in the factors that form the net profit for 2013-2014 at OJSC “Surgutneftekhim”.

Consider the second method of evaluation and analysis of the net profit of the enterprise.
Statistical method for analyzing the net profit of an enterprise
To assess the future size of net profit, various forecasting methods can be used: linear, exponential, logarithmic regression, neural networks, etc. The figure below shows the net profit forecast based on an analysis of the change in the indicator over 10 years. Forecasting was carried out using linear regression, which showed a downward trend in 2011. The accuracy of forecasting economic processes using linear models has an extremely low degree of reliability, so the use of linear regression can serve more as a guideline for the direction of profit change.

Comparison of net profit with other performance indicators of the enterprise
In addition to evaluating and calculating the net profit of an enterprise, it is useful to conduct a comparative analysis with other integral indicators that characterize the efficiency and effectiveness of the enterprise. These indicators include: sales revenue (net of VAT) and net assets. Net assets show the financial stability of the enterprise and its solvency, revenue reflects its production and sales performance. The figure below shows a graph of a large Russian enterprise OJSC ALROSA and the ratio of its three most important indicators. As can be seen, there is a close relationship between them, in addition, it can be noted that the growth of the net assets of the enterprise is positive, this indicates that the funds are directed to expand production capacities, which in the future should increase the amount of net profit received.

Is a company's credit rating and net profit related?
In my study, I analyzed the relationship between the amount of net profit for the Rosneft enterprise and the credit rating of the international agency Standard & Poor's. There is a close relationship and correlation shown in the figure below - this proves the importance of such an indicator as net profit as a criterion for investment attractiveness not only in the national space, but also in the international arena.

Summary
Net profit is the most important indicator of the effectiveness and efficiency of the enterprise. Net profit reflects investment attractiveness for investors, solvency for creditors, sustainable development for suppliers and partners, efficiency/performance for shareholders and owners. For the analysis of net profit, two methods are used: factorial and statistical. Based on the factor analysis method, the absolute and relative impact of various indicators on the formation of net profit is estimated. The statistical method is based on forecasting time series of changes in net profit. The study of the tightness of the relationship between the credit rating of the international rating agency Standard & Poor's proves the importance of the net profit indicator in assessing an enterprise in the international financial arena.
- Deadpool - Troubleshooting
- Won't start How to Survive?
- What to do if bioshock infinite won't start
- Walkthrough Nancy Drew: Alibi in Ashes
- Spec Ops: The Line - game review, review Spec ops the line crashes on missions
- Room escape level 1 walkthrough
- Processing tomatoes with boric acid How much will 2 grams of boric acid
- Cucumber Grass (Borago)
- Bioinsecticide Lepidocid: purpose, properties and application procedure Lepidocide waiting period
- How to change the language to Russian in steam
- Dendrobium noble: room care
- Morphology of plants general concepts - document
- Planting, propagation and care of bamboo at home, photo Growing bamboo from seeds
- How to strengthen the cellular signal for the Internet in the country
- Sanskrit reveals the forgotten meaning of Russian words (2 photos)
- The oldest language Sanskrit programming language of the future Dead language Sanskrit
- Who has dominion over all the earth?
- Symbols and amulets of Masons The famous Masonic amulet for money
- Hekate's father. Dark goddesses. Origin and genealogy
- nord wind airline fleet